Top 8 Telemedicine Trends and Technologies in 2025
In this article, we’ll draw on the insights and expertise of our software architects at TATEEDA to forecast the future of telemedicine and telehealth, exploring the key technology trends shaping remote healthcare delivery in 2025, both in the United States and around the world.
And no, we don’t have a crystal ball, but we do have some pretty smart medical software specialists on our team who are capable of helping you implement some of these trendy healthcare technologies!
As the old saying goes, “Necessity is the mother of invention,” and recent challenges have accelerated the shift toward more preventive, mobile, and adaptable healthcare approaches. For example, integrating custom remote patient monitoring (RPM) applications with IoT health devices enables real-time tracking of patient vital indicators for data-driven interventions or corrections as required by protocols.
Telemedicine future trends, like AI-aided telehealth software, empower a wide range of professionals—primary care doctors, psychologists, pharmacists, health coaches, and even family members—to participate in distant care coordination, extending to social workers, dietitians, and emergency responders for comprehensive virtual care, without spending countless hours commuting to hospitals and medical centers.
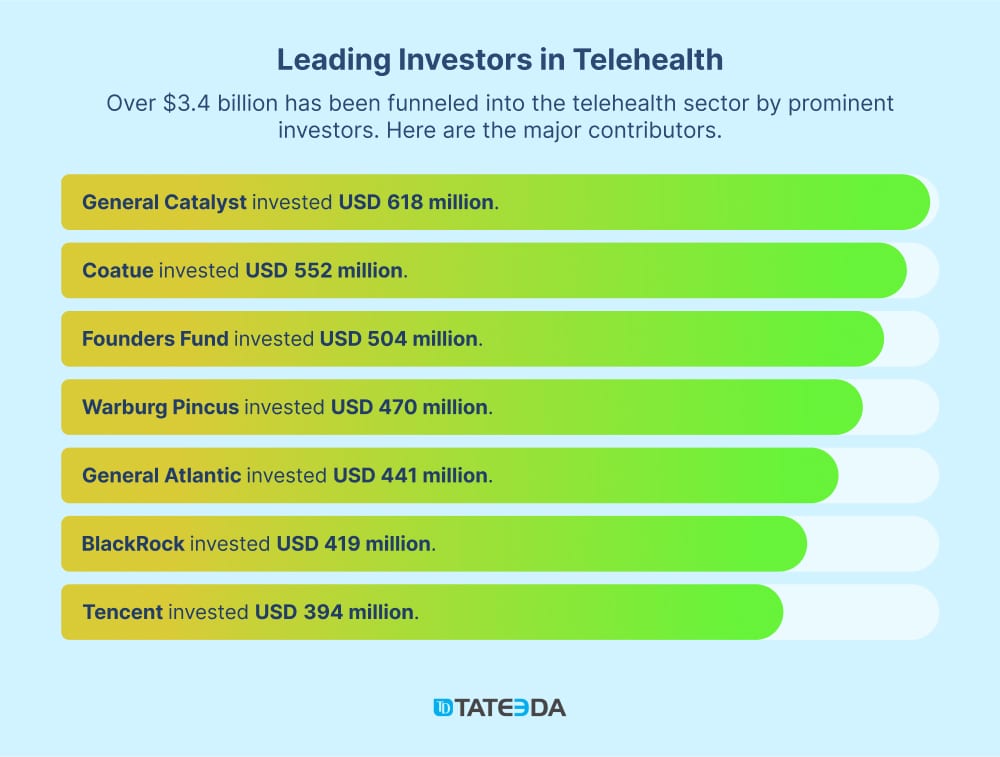
| Why are we competent to speak about telemedicine market trends? TATEEDA is a custom software development company from San Diego, successfully operating R&D resources in many locations since 2013. Our team offers deep expertise in designing and building custom solutions for telehealth consulting and remote patient monitoring. As a healthcare IT consulting company, we assist healthcare organizations in implementing advanced telemedicine technologies to enhance patient care and operational efficiency. We’ve nurtured long-term partnerships with several U.S.-based health tech companies, including those offering telepharmacy and remote electronic data capture tools, such as health condition and symptom self-assessment surveys. In this article, you’ll find case studies presented in the context of modern telehealth trends. If you need immediate consulting, please let us know ⇒ |
Interest in telemedicine continues to rise, with online doctor consultations projected to increase by 13.7 million between 2024 and 2028, an 11.74% growth. This trend reflects a preference for cyber consultations, with over 50% of U.S. patients finding virtual visits more convenient than traditional ones.
Will Telehealth Truly Be Accessible to All Patients by 2025?
The future of telemedicine will be shaped not just by technology but also by empowering users to benefit from these superb advancements while ensuring a privacy-focused and evidence-based approach. Patients must learn to navigate online platforms, understand health informatics, and use connected devices confidently.
Telemedicine’s value lies in simplifying access to healthcare through tools like cloud-based EHRs, telepharmacy, and e-prescribing, making services more accessible for distant/isolated or immobile patients while reducing barriers to timely care.
Looking ahead, improving digital health literacy and making telehealth solutions easier to use will be crucial as more people rely on telehealth tools…
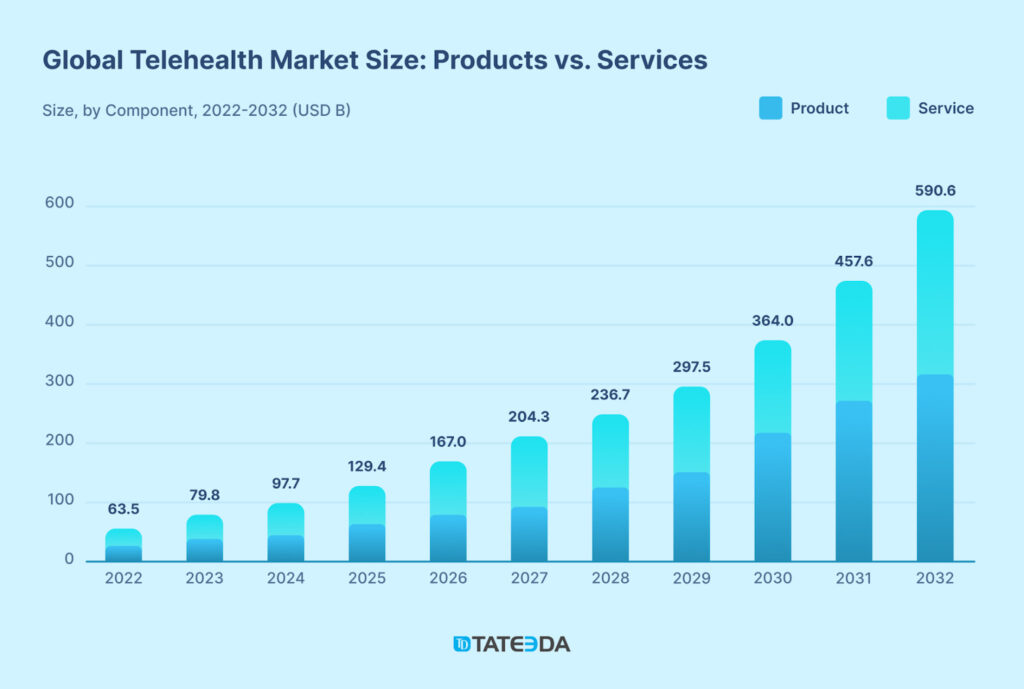
Let’s now review all the modern telemedicine trends one by one:
Table of Contents
Trend #1: Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) for Proactive and Home-Based Healthcare
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) has quickly become a blockbuster in American healthcare, especially when it comes to managing widespread chronic disorders, like diabetes, supporting recovery after surgery, and providing care for the elderly.
Close to 20% of large healthcare facilities in the U.S. have already jumped on the RPM bandwagon, and it’s no surprise—nearly 90% of patients reported that they experienced some form of remote healthcare in the past year.
With RPM-related claims skyrocketing by 1,300% between January 2019 and November 2022, it’s clear that this technology is a fundamental medical tech trend. So far, so good—the future of telemedicine technology is bright: RPM is a pie that everyone seems to have a finger in, with healthcare providers, tech companies, and patients all eager to benefit from its potential to improve medical service delivery.
?? Specialists treating chronic conditions are the main users of RPM. Internal medicine doctors lead, representing 28.7% of claims, followed by cardiologists at 21.3% and family practitioners at 19.4%.
“These numbers are not surprising at all, given the need for ongoing monitoring of conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and chronic lung disorders—conditions that are truly a matter of life and breath for many patients in the U.S.”
— Andrew G., TATEEDA’s Health Tech Architect
The strength of RPM lies in the continuous tracking of patient biometric data through wearable devices and the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT). Whether custom software for remote monitoring of heart rate, glucose, or blood pressure, RPM helps medical professionals keep an eye on vital signs without the patient needing to visit a clinic in-person. Here’s what makes it effective:
- Real-time data collection: Tools like wearable ECGs, pulse oximeters, smart scales, and continuous glucose monitors (CGM) constantly gather health metrics.
- Immediate alerts: When data raises red flags, RPM systems send real-time alerts to providers for quick action.
- Patient empowerment: Through the development of custom mHealth apps and patient dashboards, patients actively engage in their health management.
- Convenient home-based care: RPM enables quality care from the comfort of home, reducing the need for frequent office visits.
Example of RPM in Action
RPM’s ability to facilitate timely interventions can significantly reduce hospital visits. For instance, take TATEEDA’s work on the Ventrilink project: it’s a perfect example of how cloud-based platforms and remote diagnostics can transform care for heart failure patients.
As we look ahead, seamless data transmission and real-time monitoring aren’t just part of the future of telemedicine technology—they’re setting the standard for patient care and making life easier for healthcare providers.
Trend #2: Personalized Digital Therapeutics (DTx)
Personalized Digital Therapeutics (DTx) represents a huge transformative leap in how we manage chronic illnesses, which are projected to account for 84% of global deaths by 2030. These solutions go beyond generic treatments, offering personalized, data-driven interventions that focus on each patient’s specific biogenetic profiles and complex needs.
?? Managed by skilled clinicians or medical service specialists, DTx platforms provide real-time therapeutic adjustments through handheld devices, enhancing care for multiple conditions like diabetes, mental health disorders, and cardiovascular diseases.
DTx empowers patients to manage their health proactively from home. Whether this works through tools like remote therapeutic monitoring (RTM), patient-reported outcomes (PRO), or mobile-based health interventions, these platforms provide continuous, personalized care. This trend stands out among the latest telemedicine trends by focusing on patient engagement and empowerment, reducing the need for frequent clinic visits while improving outcomes.
Key aspects of personalized DTx:
- Remote Therapeutic Monitoring (RTM): DTx platforms track patient progress in real-time using connected devices, adjusting treatment based on data collected from wearables and other health devices.
- Patient-Reported Outcomes (PRO): Patients can actively log their symptoms through digital symptom diaries, providing healthcare providers with invaluable insights into the effectiveness of treatment.
- Virtual Rehabilitation & Self-Guided Therapy Apps: These platforms offer virtual rehabilitation programs and self-guided therapy apps, enabling patients to manage their physical or mental health challenges from home, especially when in-person visits to therapists are not scheduled or unavailable for some reason.
- Psychoeducation Platforms: Mental health-focused DTx platforms provide psychoeducation and ongoing monitoring, helping patients navigate behavioral challenges with personalized support. These platforms include SilverCloud Health (offering CBT-based modules for anxiety and depression), MoodGYM (online CBT for identifying and managing unhelpful thoughts), and Woebot Health (an AI-powered tool for real-time mood tracking and CBT-based stress management).
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): Integration with clinical decision support systems (CDSS) allows healthcare providers to make data-driven decisions, improving patient outcomes through real-time insights.
Example of DTx in Action
TATEEDA GLOBAL partnered with Visiontree, a healthcare technology provider, to create a web-based electronic data capture (EDC) system for documenting Patient-Reported Outcomes (PRO). The platform uses digital symptom diaries and self-management apps to collect real-time patient data via secure electronic forms, helping healthcare providers track patient progress throughout treatment.

This collaboration ensures healthcare organizations can capture accurate, structured data to enhance care and research outcomes. TATEEDA’s work with Visiontree is a prime example of how digital therapeutics drives the future of telemedicine and telehealth to more patient-centered care, turning digital symptom diaries and self-management apps into powerful tools for real-time health management and precisely individualized treatment strategies.
Trend #3: Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Telemedicine
Among the major telemedicine trends, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is turning the tables on how remote healthcare is delivered, enabling smarter, more accessible, and more proactive solutions. Global flagship companies like IBM Watson Health, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud AI, and Oracle AI are leading the path for wider cognitive computing adoption in telemedicine.
??⚕️ Their cloud platforms empower healthcare providers to tackle advanced tasks such as real-time health condition forecasting, adaptive patient diagnostics, and personalized treatment recommendations based on multiple subtle factors. The global AI healthcare market is projected to reach over $45 billion by 2026, opening up endless possibilities for new AI use cases in telemedical practice, investments, and discoveries.
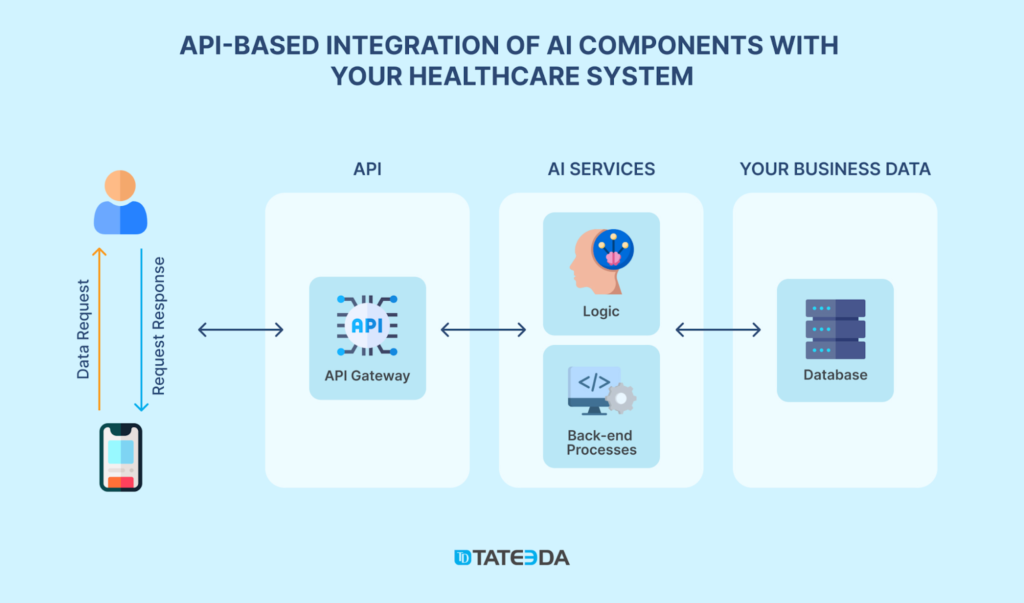
AI-fueled Future Trends in Telemedicine:
- Diagnostics and Imaging: AI-aided algorithms enhance diagnostic accuracy, achieving sensitivity rates of 87-92% in analyzing CT scans and X-rays, which improves precision by up to 40%. These tools enable earlier detection of conditions like tumors and streamline medical research processes through automated image segmentation, reducing the workload on human radiologists.
- Predictive Analytics and Cognitive Computing: AI applies cognitive computing to learn and predict health risks, analyzing health data patterns to empower early interventions and develop personalized treatment plans for patients of all ages and social groups.
- Intelligent Patient Monitoring: Combined with wearables or smart implants, AI supports intelligent patient monitoring with the functionalities of real-time tracking and automated health coaching when irregularities are detected.
- AI-Powered Decision Trees and Care Coordination: AI-powered decision trees guide clinical decisions, assisting with AI-driven care coordination and online bots suggesting appropriate follow-ups. This accelerates medical decision-making and makes healthcare more accessible and cost-effective, as AI enables medical professionals to treat significantly more patients simultaneously.
- Digital Twin Health Modeling: AI builds virtual replicas of a patient’s health, using real-time data from sources like wearables and medical records. These digital twins help predict health issues, simulate treatment outcomes, and fine-tune care plans, making medical interventions more precise and personalized. For example, digital twins can help with better heart treatments by simulating arrhythmias and adjusting ICU ventilation settings based on lung mechanics. They also use genomic data to foresee disease risks and support preventive strategies specific to each patient’s profile
As AI continues to advance, it is transforming the future of telemedicine from a reactive approach to a proactive, patient-centered model, delivering more efficient and adaptive healthcare solutions while promising longer, healthier lives for everyone.
Trend #4: Big Data and Analytics in Telehealth
“The global volume of healthcare data is expected to reach over 10,000 exabytes by 2025, with the U.S. accounting for about 30% of this total.”
— Victor K., TATEEDA’s Data Engineer
Thanks to this massive accumulation of health records in the U.S. and other developed countries, Big Data and Analytics have emerged as one of the most impactful telehealth trends, enabling advanced medical data-mining techniques that uncover deeper patterns in pandemics, diseases, and other health-related phenomena.
The vast amount of clinical information on medical cases generated by electronic health records (EHRs), captured from wearable/portable devices, and obtained via remote patient monitoring technologies has paved the way for truly data-driven decision-making in healthcare, supported by evidence from millions of medical cases observed in the U.S. and worldwide.
How Big Data is Used in Telehealth
Big Data is profoundly changing the game in telehealth’s latest trends, allowing healthcare providers to dig deeper into patient medical profiles, visualize healthcare data in many ways, and spot important patterns that might have gone unnoticed before. Here’s how it’s being used:
- Predictive Analytics for Early Intervention: Using time-series analysis and multivariate data analysis, Big Data helps predict future health events, enabling timely interventions based on patterns detected in historical data.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Digital phenotyping and clinical outcome tracking allow for tailored treatment scenarios that account for individual health data, including family genetics, lifestyles, and real-time biometrics collected from pro-grade wearables and biosensors.
- Remote Patient Monitoring and Alerts: Wearable tech data mining supports continuous monitoring, with anomaly detection algorithms that identify irregularities and trigger alerts for healthcare providers to act promptly.
- Population Health Management: Data fusion techniques aggregate information from different patient groups, uncovering trends to optimize preventive strategies and resource allocation.
- Operational Efficiency: Prescriptive analytics improve resource management and streamline telehealth workflows by analyzing data patterns to recommend the most efficient course of action.
The Architecture of Big Data and Telehealth Integration
According to our health tech software architects and experts, this is how the integration of telehealth and Big Data operates:
| Layer | Description |
| Data Sources | Collects information from EHRs, wearable devices, medical imaging, lab results, and telehealth consultations for health data integration. |
| Cloud-Based Data Storage | Uses cloud-based data storage solutions such as data lakes and warehouses to securely store and manage structured and unstructured data. |
| Data Processing and Analytics | Leverages real-time decision support tools, anomaly detection, and multivariate data analysis to transform raw data into actionable insights. |
| Integration Layer | Utilizes health data integration platforms and APIs to connect analytics engines with telehealth systems, ensuring seamless data exchange. |
| Data Visualization Dashboards | Provides data visualization dashboards to display insights and trends, helping clinicians make informed decisions and monitor clinical outcomes. |
Example of Big Data in Telehealth
The U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs uses Big Data analytics in telehealth to monitor veterans’ health through remote devices and EHRs. This approach helps predict health risks and provides timely care, significantly reducing hospital readmissions.
As one of the future trends in telehealth, integrating Big Data with telemedicine is essential for enhancing patient outcomes, streamlining operations, and enabling data-driven healthcare practices.

Trend #5: Telepharmacy
Telepharmacy is becoming a pivotal telehealth component, transforming how pharmacy services are accessed and delivered. Thanks to the rapid growth in digital health technologies and increasing patient demand, it’s clear that telepharmacy now offers crucial services like…
- medication consultations
- automated refills
- remote dispensing
- making pharmacy care more accessible, especially in rural or underserved areas.
Why Telepharmacy is Gaining Traction
As healthcare increasingly shifts to digital, the demand for remote services has surged. For instance, as far back as 2020, more than 70% of patients expressed a preference for online healthcare access, which means that telepharmacy is well-positioned to meet this growing expectation. Regulatory changes have further supported this trend in 2025, enabling practices like digital prescription transfer and remote treatment adherence, which are vital for effective chronic care management.
How Telepharmacy is Used in Telehealth
Telepharmacy custom software dev services encompass various innovative approaches that go beyond traditional pharmacy roles:
- Virtual Consultations and Medication Guidance: Since over 60% of U.S. adults take prescription drugs regularly, it’s clear that virtual consultations can significantly improve access to medication guidance, ensuring patient safety through tools like virtual drug interaction alerts.
- Remote Dispensing and Automated Solutions: Thanks to advancements like automated dispensing cabinets, pharmacies can now provide remote dispensing in areas where access is limited, making it easier for patients to get their medications promptly.
- Medication Therapy Management (MTM): Given that chronic illnesses account for 90% of healthcare costs in the U.S., it’s clear that MTM through telepharmacy can help reduce these costs by enabling pharmacists to use predictive analytics for prescriptions to anticipate medication needs and prevent complications.
- Prescription Synchronization and Refill Management: As 20-30% of patients struggle with medication adherence, automated refills, and prescription synchronization services ensure they stay on track, which might be surprising but can reduce hospital readmissions.
- Advanced Digital Tools: With the growing integration of clinical data, digital drug labeling, and real-time decision support, telepharmacy provides patient-specific care, adapting quickly to each patient’s changing health status.
Example of Telepharmacy in Practice
A Canadian pharmaceutical company reached out to us to streamline its operations, and we stepped in to help by developing a web-based platform that automated the entire process of ordering, processing, and shipping prescription drugs for their U.S. partners.
“The system took things to the next level by making data management simpler and adding shipment tracking. It didn’t just make everything run smoother—it actually opened the door for new business opportunities, showing how telepharmacy can transform the way pharmaceutical operations work.”
— Igor K., TATEEDA’s Senior Developer
Trend #6: AR/VR in Telehealth
According to TATEEDA’s telemedicine software experts, AR/VR is emerging as a transformative force in telehealth, with the U.S. market for these technologies projected to reach $11.3 billion by 2030, growing at a 16.8% CAGR.
“We’re seeing more and more AR/VR adoption in healthcare because the demand for immersive solutions just keeps growing. Whether it’s for planning surgeries, managing chronic pain, or training staff, the need for this kind of technology is really taking off.”
— Anastasia M., TATEEDA’s Front-End Tech Team Lead
For instance, Hoag Hospital has deployed AR/VR for everything from surgical preparation to staff stress relief, while the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) uses VR for managing PTSD and chronic pain, with significant success.
How AR/VR is Used in Telehealth
AR/VR technologies are being employed across various telehealth applications:
- Training and Education: AR/VR provides simulated training modules for healthcare professionals, using 360-degree video and spatial computing to replicate real-world scenarios.
- Chronic Care Management: VR platforms help manage chronic conditions by delivering therapeutic experiences, such as AppliedVR’s RelieVRx for lower back pain. Programs include tactile internet features that simulate physical sensations.
- Rehabilitation and Telesurgery: AR assists with virtual ward rounds and telesurgery, allowing for remote consultations and precise anatomical visualization during procedures.
- Surgical Planning and Assistance: AR provides real-time stereoscopic 3D imaging to help surgeons visualize anatomy during operations.

How AR/VR is Implemented in Telehealth
The following table outlines the methods suggested by TATEEDA’s experts for integrating AR/VR into telehealth systems:
| Implementation Method | Description |
| 3D Bioprinting and 3D Scanning Technologies | Creates realistic anatomical models for surgical planning and patient education. Implementing this requires specialized 3D bioprinters and scanning devices like MRI and CT scanners to capture detailed anatomical data. High-resolution 3D printing materials are also essential for creating accurate replicas. |
| Biometric Gateways and Spatial Computing | Provides secure authentication and immersive experiences by tracking user movements and biometric data. This method requires biometric sensors, such as fingerprint readers or facial recognition cameras, combined with spatial computing hardware like motion sensors (e.g., Microsoft Kinect) and AR headsets to capture real-time environmental data. |
| Zero Latency Streaming and WebXR | Enables seamless real-time interactions in VR environments for remote monitoring and training. Implementation involves using low-latency streaming protocols (e.g., WebRTC) and WebXR-compatible browsers to support mixed reality experiences. It also requires high-bandwidth internet connections and cloud-based servers for data processing. |
| Synthetic Data | Uses simulated patient scenarios for training, ensuring ethical practices with bioethical governance. This approach involves generating artificial datasets using AI algorithms and machine learning models to mimic real-world health data. Synthetic data platforms and software tools (e.g., Hazy or Gretel.ai) are necessary for creating realistic patient scenarios while protecting privacy. |
| Tactile Internet and Stereoscopic 3D | Enhances simulations with touch and depth perception, aiding physical therapy and surgical precision. It relies on haptic feedback devices, such as gloves or suits, paired with stereoscopic 3D displays or AR/VR headsets to create a realistic sense of touch and depth in virtual environments. |
| Virtual Ward Rounds and Telesurgery | Facilitates remote consultations and surgical planning with 3D visualization for better decision-making. Implementing this requires telepresence equipment, high-definition cameras, robotic surgery tools, and real-time communication platforms to support remote interactions and provide detailed views of surgical fields. |
| Anatomical Visualization | Uses AR to display 3D models of anatomy during procedures, offering real-time guidance for surgeons. This requires AR-enabled devices like Microsoft HoloLens or Magic Leap, software for rendering 3D anatomical models, and tracking sensors to align the visualizations accurately with the patient’s body. |
Trend #7: Wearables and Telehealth mApps
“Wearables coupled with the newest mobile health app trends are taking off in telehealth because people want real-time insights into their health, whether it’s heart rate, blood sugar, or sleep. These tools help make healthcare an everyday part of life, not just something you think about when you’re ill.”
— Slava K., TATEEDA’s Health-Tech Architect
Wearable tech, smart implants, or medical gadgets connected to mobile health apps (mApps) are gaining serious popularity as more people look for convenient ways to constantly monitor their health and stay synchronized with their healthcare providers 24/7. The global wearables market is projected to surpass $118 billion by 2028, driven by the demand for devices that provide real-time data exchange and insights.
Major players like Apple, Fitbit, and Garmin continue to introduce sophisticated pro-grade gadgets with new features such as cardiac rhythms monitoring, blood oxygen tracking, fall detection, and emergency alerts, which makes wearables essential tools in complex chronic care management and daily wellness for a wide range of patient groups.
How Wearables and Telehealth mApps Are Used
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Wearable devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers collect data such as heart rate, steps, and blood glucose levels, and send this information to telehealth apps synchronized with server applications in healthcare providers to process and review. This kind of biometric data analysis is crucial for managing chronic conditions at home and detecting health issues early.
- Chronic Care Management: In patients with long-term health conditions, wearables, and mApps continuously monitor vital signs to generate alerts or send notifications to authorized medical professionals when measurements deviate from normal ranges, allowing for timely interventions.
- Lifestyle and Wellness Tracking: Telehealth mApps often integrate with wearables via wireless networks to promote healthier lifestyles by tracking and reporting physical activity, sleep patterns, and diet. Some apps offer augmented cognition features for personalized health recommendations and insights based on data collected from wearables and clinical records of a patient (so multiple health specifics can be taken into account for better outcomes.)
- Data Integration and Analytics: Wearables can sync with smart health records, allowing up-to-date data to be stored and analyzed within a patient’s medical history. This integration supports more data-driven telehealth workflows and predictive analytics for healthcare providers, while patients can access their data via custom web or mobile patient portal solutions.
- Rehabilitation and Recovery: Wearables like motion sensors and smartbands help track patient progress during physical therapy or post-surgical recovery, providing valuable data for healthcare teams to adjust treatment plans.
Implementing Wearables and mApps in Telehealth
For wearable tech to work seamlessly with telehealth, certain components are required:
| Component | Description |
| Biometric Sensors | Used in wearable devices to measure various health metrics, such as heart rate, glucose levels, or blood pressure. Examples include optical heart rate sensors and accelerometers. |
| Data Synchronization Technologies | Ensure real-time data exchange between wearables and telehealth apps through Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or cellular networks, allowing for continuous monitoring. |
| mHealth App Integration | mApps should be compatible with both iOS and Android platforms, providing features like push notifications, teleconsultation, and real-time decision support. |
| Cloud-Based Data Storage | Wearables often use cloud services to store large amounts of health data securely, supporting zero latency streaming and enabling healthcare providers to access patient data from anywhere. |
| Predictive Analytics and AI | Wearables and mApps leverage machine learning and predictive algorithms to analyze collected data, offering insights that can predict health risks or recommend lifestyle changes. |
Examples of Wearables and mApps in Action
- Apple Watch: Offers health monitoring features like ECG, blood oxygen level tracking, and fall detection, and integrates with Apple Health for comprehensive data analysis.
- Dexcom G6: A continuous glucose monitoring device that sends real-time glucose readings to a smartphone app, helping diabetes patients manage their blood sugar levels.
- Whoop Strap: A wearable designed for athletes that measures sleep quality, recovery, and strain to optimize performance.
With wearables and telehealth mApps forging the future of telemedicine and telehealth, it’s clear that healthcare is becoming more accessible and integrated into daily life, pushing forward telemedicine market trends and enabling more proactive patient care.
Trend #8: Medical Drones
“Medical drones are revolutionizing the way healthcare is delivered, especially in remote areas. From delivering prescription drugs to providing emergency support like defibrillators and survival gear, drones make rapid, contactless healthcare possible where it wasn’t before,”
— Slava K., TATEEDA’s Health-Tech Architect.
The adoption of medical drones is quickly emerging as one of the most impactful telemedicine industry trends, especially in regions where traditional healthcare delivery is challenging. The ability of drones to perform contactless delivery of medical supplies, medications, and emergency equipment offers a faster and more efficient solution for critical situations. With the global drone market in healthcare projected to grow at a 24% CAGR over the next five years, the role of drones in telemedicine latest trends is expanding significantly.
How Medical Drones are Used in Telehealth
- Prescription and Vaccine Delivery: Drones can deliver medications, vaccines, and other medical supplies to areas that are difficult to access, making them essential for last-mile vaccine delivery and immunization campaigns.
- Emergency Medical Response: In critical situations, drones equipped with defibrillators or survival gear can be dispatched to provide life-saving support. Compact ambulance drones even offer real-time emergency medical communication with healthcare providers.
- Epidemiological Mapping and GIS Integration: Communication relay drones assist in gathering live data feeds for epidemiological mapping, helping track disease outbreaks and coordinate responses.
- Autonomous Navigation and IoMT Integration: Using autonomous navigation systems, drones can connect with the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) to provide data for drone telemetry, facilitating seamless integration into healthcare networks.
- Surgical and Medical Supply Delivery: For hospitals or disaster zones, drones can deliver surgical supplies, blood products, and essential equipment, ensuring timely support even when roads are inaccessible.
Implementing Medical Drones in Telehealth
To effectively integrate medical drones into telehealth solutions, various technologies and components are required:
| Component | Description |
| Command and Control Software | Manages drone operations, flight paths, and payloads. Must include real-time tracking and logistical coordination AI for seamless delivery. |
| Communication Relay Drones | Provide data transmission and communication support, extending the reach of emergency medical communication networks. |
| Autonomous Navigation Systems | Enable drones to operate independently using AI algorithms for EVTOL (Electric Vertical Takeoff and Landing), avoiding obstacles and navigating complex terrains. |
| GIS Mapping Integration | Utilizes GIS mapping for precise delivery routes, especially important for tasks like epidemiological mapping or delivering to remote locations. |
| IoMT Drone Integration | Connects drones with healthcare IoT devices to share data through drone telemetry, enabling real-time monitoring and response. |
| Compact Ambulance and Defibrillator Drones | Drones equipped with life-saving devices such as defibrillators for cardiac emergencies offer immediate assistance before medical personnel arrive. |
| Live Data Feeds and Telemetry | Provides real-time information from the drone, including location, environmental conditions, and status updates on deliveries. |
| Survival Gear Airdrops | Capable of delivering essential survival items like first aid kits or water to disaster-stricken areas, ensuring rapid assistance. |
Examples of Medical Drones in Action
- Zipline: This company uses drones to deliver blood products, medications, and vaccines in remote regions of Africa, ensuring timely medical access where traditional means fall short.
- Wingcopter: Provides contactless delivery of medical supplies, including COVID-19 vaccines, to rural and hard-to-reach communities.
- Matternet: Partners with hospitals in Switzerland and the U.S. to deliver surgical supplies and patient samples, reducing turnaround time significantly.
With medical drones paving the way for the bright future of telemedicine and telehealth, they are setting brand new standards for rapid response and healthcare delivery. These advancements reinforce telemedicine market trends toward more agile, technology-driven solutions.

In Conclusion
Let’s recap the pivotal telehealth trends we’ve unpacked: Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM), Personalized Digital Therapeutics (DTx), AI-driven tools, Big Data, AR/VR, wearables, and medical drones. These innovations are not just reshaping healthcare; they’re personalizing and streamlining it, making health management a part of our everyday lives.
Are you ready to step up and integrate these technologies, or will you watch from the sidelines? Telehealth is becoming indispensable, and the stakes for staying current are high. Companies slow to adopt may find themselves at a disadvantage in swiftly changing healthcare market stats.
At TATEEDA, we’re keen to guide you through this transition. Our robust team of over 100 senior engineers has the breadth of expertise to support complex projects, particularly in the U.S. health tech sector. While we’re still navigating the new territories of AR/VR and drone technology, our commitment to growth means we’re constantly exploring innovative avenues to support your needs.

Reach Out Today for a Free Consultation and Estimate
Embracing telehealth with TATEEDA means staying ahead in the game and ensuring your healthcare solutions are not just current but leading edge.








![Best AI Development Companies [USA] Title Image](https://tateeda.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/Best-AI-Development-Companies-for-the-United-States-1-2.jpg)
