Cyber Security in Healthcare: The Methods & Importance of Medical Data Protection

How crucial are methods of data protection in healthcare companies, startups, and IT products?
In this guide, we’ll discuss all potential cyber threats, challenges, medical cybersecurity requirements, and specific healthcare data-protection measures to be implemented in any health organization: hospitals, clinical centers, ERs, offices, and digital health businesses in the United States and worldwide.
| ⚠️ If your company requires immediate help with auditing and implementation of cyber security in the healthcare industry, book a free call with our skilled health data protection engineers ⟶. |
The U.S. government maintains a very precise definition of Protected Health Information (PHI), the major principles of which are explained in the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). This document sets a strict approach and standards for safe data management and operations with PHI.
According to HIPAA rules, the concept of PHI refers to almost all classes of both physical and electronic health records, such as…
- Patient demographics
- Contact details and IDs
- Medical histories and examination results
- Lab tests and body scans
- Mental health conditions
- Insurance status and transactions
- Drug prescriptions and more.
Why is Cybersecurity Important in Healthcare?
| The importance of data security in healthcare stems from the prerequisites and rules articulated by the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). HIPAA was developed on the basis of the U.S. Constitution and interprets human rights principles, privacy laws, digital property-protection rights, and other modern legitimacy fundamentals. |
This means that all sensitive personal and medical data pieces must be carefully managed and never extracted without special permission. Medical data is available for authorized and protected access ONLY.
At the same time, according to the legal framework outlined by the HIPAA, authorized healthcare professionals, healthcare process operators, and patients (as sole legal data owners) are to be provided with exclusive data-management rights and appropriate technology tools for accessing PHI securely.
What Is the Current Situation with Cybersecurity in the Healthcare Industry?
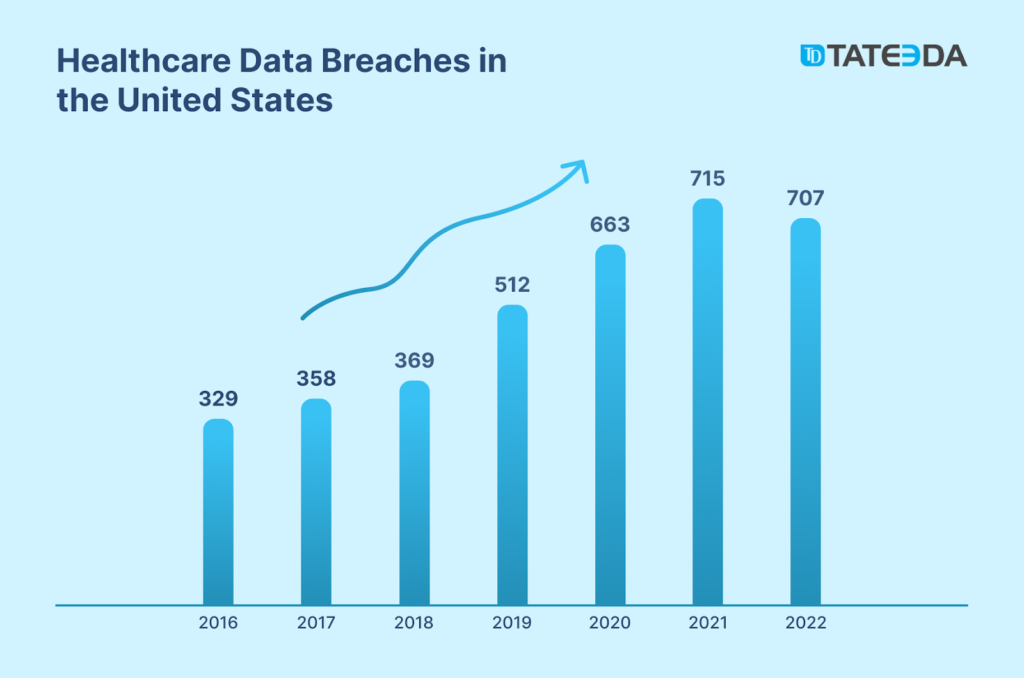
Despite well-conceived legislation, American healthcare has suffered from numerous medical data breaches, security violations, and cases of misuse. According to official reports provided by the HHS Office for Civil Rights, more than 5000 healthcare data breaches occurred between 2009 and 2022, leading to the disclosure of 382,262,109 health records. This figure far exceeded the U.S. population during this time interval.
The patient data-violation episodes included both IT security incidents and deliberate hacking efforts. During a six-year period (2016-2022), the rate of medical data violations more than doubled, as shown on this graph:
Why would someone attempt to steal health data from medical companies and organizations? The potential spectrum of criminal activity and manipulation involving sensitive medical data falling into the wrong hands is extremely broad:
- Bank ID and insurance fraud
- Espionage and persecution
- Unauthorized access to prescription drugs
- Blackmail and extortion
- Black hat marketing
- Stolen data-dealing in the darknet.
Healthcare data breaches can entail severe and costly consequences for patients and healthcare providers, including financial loss, withdrawal of medical practice licensure, and further legal action for failing to protect patient information.
Protecting sensitive medical information from cybercriminals requires robust healthcare data security measures to safeguard against attacks and prevent any unintentional data breaches. Take a minute to learn more about our company before you proceed to the next section, where we will describe the most common cyber security threats in healthcare:
| ? TATEEDA GLOBAL is a custom medical software development company based in San Diego, CA with more than 10 years of experience successfully enhancing cybersecurity for healthcare organizations and startups in the U.S. and worldwide. If you are seeking data protection, healthcare consulting, or software development services, book a free chat with one of our experienced health-tech engineers: ⬇️ |

Slava Khristich
Healthtech CTO
Based in San Diego, Slava knows how to design an efficient software solution for healthcare, including IoT, Cloud, and embedded systems.
Table of Contents
The 7 Most Common Threats to Healthcare Data
Here is a list of the top 7 cybersecurity threats targeting healthcare data, which all medical organizations must be prepared to repel. Despite the fact that these cyber threats have been recognized by security analysts for a while, they are still highly effective and pose a serious danger to valuable medical data. Let’s learn about them:
#1. Phishing Emails Hitting a Medical Organization’s Inbox
Social engineering is a very common cyber security risk these days. The majority of patients and medical professionals have faced this phenomenon at least once. Phishing tactics include felonious emails or messages designed to trick recipients into clicking fraudulent links and/or revealing their sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, IDs, documents, and more.
Phishing emails usually come under the guise of email spoofing methods, which makes this type of cyberattack highly effective. About 18% of painful healthcare data breaches happening every year are the result of phishing attacks or email account hijacking.

#2. Malware Spreading in Healthcare Networks
Malware (a.k.a scumware or thiefware) is a large family of harmful programs: viruses, trojans, spyware, and coin miners. These cybersecurity threats in healthcare are designed to penetrate healthcare system security barriers and compromise data integrity to benefit cybercriminals. Healthcare organizations with poor IT security or insufficient data-protection tools are highly vulnerable to all types of malware attacks.
These attacks can start as phishing attempts, with users accidentally clicking dangerous links and transmitting malware to their devices from the Internet. Further scenarios may vary according to malware type. Computer viruses can spread across healthcare organizations’ computers and network nodes incrementally, incurring significant damage by interfering with critical medical software operations. This can lead to theft or destruction of sensitive data in bulk.
#3. Legacy Healthcare System Loopholes ?️
The number of outdated healthcare applications being used in hospitals, clinics, offices, and medical centers is surprisingly huge. It was discovered that almost 83% of healthcare IoT devices in the United States are driven by vulnerable operating systems that keep around 98% of sensitive medical data transactions exposed or poorly encrypted.
This opportunity encourages hackers to take advantage of loopholes in obsolete healthcare systems. In this type of individualized intrusion scenario, cybercriminals can break through many barriers and do a lot of harm before they even get noticed. This threat can be reduced by the implementation of healthcare system upgrades, updates, patches, replacements, and other well-crafted solutions.
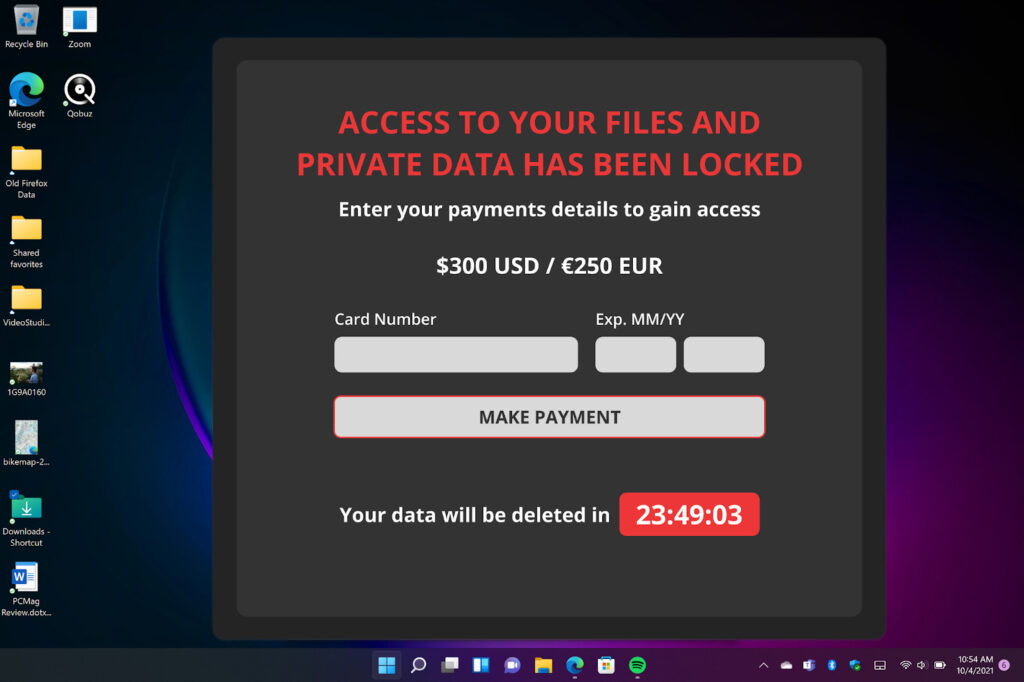
#4. Ransomware Paralyzing Clinical PCs
Ransomware is a subcategory of scumware/malware that is used to infiltrate a computer OS (or web browser) to arrest system functionality. After ransomware blocks a system or computer, it generates an invasive pop-up message that demands payment from the victim to unblock access. These attacks are highly disruptive, and can cause significant financial and morale-based losses to healthcare organizations, employees, and patients. This type of attack is usually spread through healthcare employee interaction with phishing emails or dangerous websites.
#5. Medical Organization Insider Threats
This situation occurs when medical company employees intentionally or unintentionally disclose sensitive data. The threat can be difficult to detect and prevent, and as with any threat involving human factors, it cannot be avoided completely. That’s why organizations need to implement efficient access control routines, role hierarchy, and appropriate HR policies, including employee reputation-screening and privacy data protection training.
Learn more here: ➡️ Medical Staffing Software Compliance: How to Achieve HIPAA Validity
#6. Healthcare Website Under DDoS Attack ?️
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks involve flooding a healthcare website or web-based system (such as a physician or patient access portal) with extreme loads of junk bot traffic from multiple sources. This overload drives it down and makes the system inaccessible to legitimate visitors. DDoS attacks can not only lead to operational downtime in healthcare organizations, but are often used as a diversion tactic to distract medical organizations’ IT staff while other attacks are carried out.
#7. Physical Theft or Loss
Physical device theft or loss (laptops, mobile phones, tablets, and USB drives) can result in harsh violation of sensitive healthcare information. Organizations must ensure that all devices containing patient data and/or user profiles constantly logged in to healthcare applications have sufficient protection to prevent unauthorized access should a device fall into the wrong hands (e.g., urgent logout and user block set from a master workstation.)

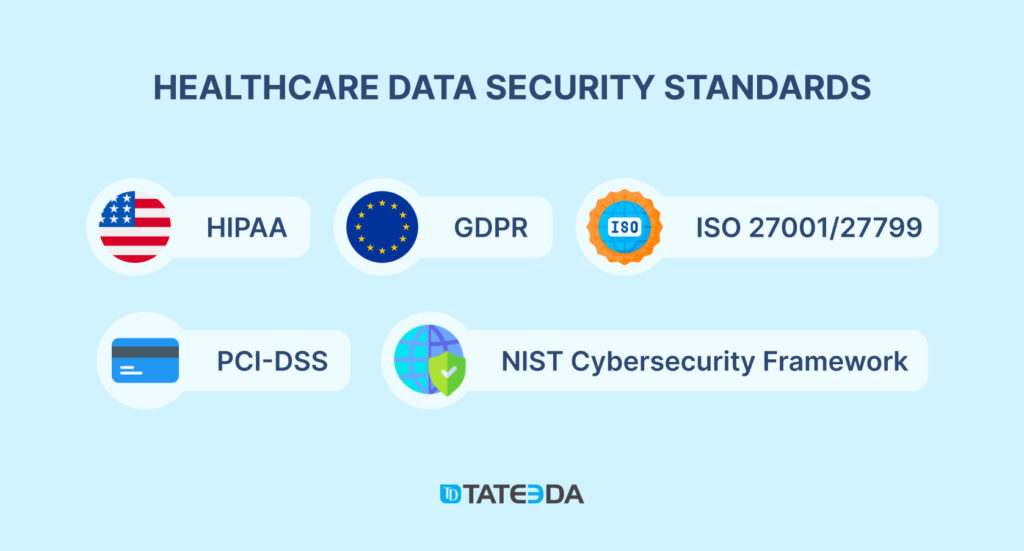
Healthcare Data Security Standards: HIPAA, GDPR, and More
Software development cybersecurity baselines must be implemented across all healthcare company IT practices. These standards of data protection in healthcare include a group of local laws and internationally recognized conventions:
HIPAA
We partially explained the role of HIPAA at the beginning of the article. HIPAA is a U.S. law establishing national standards for protecting sensitive patient health information. It requires that healthcare providers and all stakeholders exchanging medical data (insurers, labs, lawyers, etc.) implement efficient administrative, physical, and technical procedures to prevent data incidents. The point of these guidelines is to minimize the probability of data leaks and help take cyber security threats in healthcare under full control.
Here are some security precautions protocoled by HIPAA:
| Technical precautions | ✅ Transaction encryption and authorization ✅ Login control and activity monitoring ✅ Automatic log-offs for devices |
| Physical precautions | ✅ Device access control ✅ Workstation management ✅ Device protection and use monitoring |
| Administrative precautions | ✅ Train medical staff ✅ Sign BAA (business associate agreement) ✅ Document security measures ✅ Risk-management policy |
| Privacy precautions | ✅ Respond to patient requests ✅ Permission management for accessing PHI ✅ Data integrity maintenance. |
GDPR
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a regulatory framework in the European Union. GDPR governs the protection of personal data on the Internet and in electronic systems, including healthcare data management.
GDPR applies to all organizations that collect or process the personal data of E.U. citizens, including healthcare organizations. GDPR requires organizations and companies to introduce appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect sensitive medical data from hackers.
ISO 27001/27799
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provides guidelines and best-practice framework for the following:
- ISO 27001: Information security-management systems (ISMS)
- ISO 27799: Healthcare information security-management systems (HISMS)
Both ISO standards have similar values and common points with HIPAA, with the exception of a few nuances. If your healthcare software system is proven HIPAA-compliant, it’s safe to say that it’s nearly compliant with ISO 27001/27799 requirements and could potentially pass ISO accreditation procedures, if required.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides a voluntary cybersecurity framework that provides guidance for how organizations can manage and reduce cyber risks. It is widely adopted in the U.S. healthcare industry, but it’s not a must from a legal point of view. NIST outlines five pillars for how cyber threats must be handled:
- Identify (systems, gaps, threats, etc.)
- Protect (do everything to safeguard your systems against identified threats)
- Detect (monitor and keep the situation under control)
- Respond (act according to specific protocols if a breach happens)
- Recover (repair, restore data, and analyze the experience.)
PCI-DSS
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a set of security standards developed and coordinated by a council of major credit card companies (American Express, Discover, JCB International, MasterCard, Visa Inc.) This standard promotes protection for payment channels, electronic commerce, and sensitive cardholder data. Healthcare organizations that accept credit card payments must comply with PCI DSS, including secure medical billing system integrations.
| Are you interested in strengthening your healthcare data protection? TATEEDA GLOBAL offers the following services… ✅ HIPAA-compliant medical staffing development services ✅ Secure staff augmentation with well-trained developers and QA testers for hire ✅ Custom healthcare CRM system development ✅ DevOps consulting services ✅ Cloud and IT consulting in health-tech ✅ Biotech and laboratory system development ✅ PCI-DSS compliant payment system integration ✅ Secure patient portal development. Contact us today for a free consultation, or learn more about our services: ⬇️ |
Custom Healthcare Solutions
See how we can engineer healthcare software, validate your ideas, and manage project costs for you.

Steps to Implementing Medical Data Security: Best Practices for Protecting Healthcare Information
Here’s a recipe for achieving better cybersecurity in healthcare organizations. You’ll need to implement each of these methods to effectively prevent healthcare data breaches.
Step #1: Educate Healthcare Staff
The human factor, including staff negligence, poses the biggest threat to security in healthcare systems. It’s necessary to educate healthcare employees on the basics of cybersecurity and let everyone embrace responsibility for keeping patient data secure. Specialists must be well-prepared and qualified in terms of computer security before you even permit them to operate medical databases or grant access to EHR or other custom hospital management software. Additionally, an augmented computer dialog must be deployed to support employee decisions that includes:
- Hints
- Warnings
- Email scanning
- Reminders
- Quick access to emergency protocols.
Learn more: ➡️ Custom EHR Software Development Services
Step #2: Introduce Data Usage Monitoring
These practices include intelligent (usually automated) access control and activity-monitoring deployed across healthcare organization IT environments. This includes registering staff activities, user login/logout monitoring, reporting, flagging, and/or blocking suspicious activities:
- Suspicious incoming and outgoing emails or other communications
- Improper website visits and violations of web access restrictions
- Strange or unusual network activity and incoming/outgoing traffic spikes
- Suspicious system login attempts in terms of device, time, and location.
Step #3: Introduce Sufficient Medical Data Encryption
Encryption is a process that transforms readable data into an unreadable format using a ciphering algorithm and a secret key that allows data to be deciphered at the point of arrival. There exist different methodologies of data encryption that work for healthcare data protection, both in the process of transition and at rest (kept in databases.) Certain encryption methods are already incorporated in up-to-date healthcare software solutions; however, this requires additional control for legacy applications, custom solutions, and segmented systems, including various types of networking between the endpoints (like IoT networks with wireless connections.)
Step #4: Promote Security for Healthcare Mobile Devices
The process of accessing mobile devices must be controlled by multi-factor authentication, strong passwords, automatic logouts, user sign-in tracking, and forceful user account-blocking in case of physical device loss. Also, it’s important to track the physical device location, including regular tech-maintenance routines.
Learn more: ➡️ How to Develop Medical Practice Management Software: Features, Services, Use Cases
Step #5: Perform Continual Risk Assessments
Regular analysis of risk and technical maintenance programs is a must! Penetration test is one of the effective cybersecurity procedures for checking your readiness for cyberattack. This includes a strategy for detecting vulnerabilities and security gaps via recurring technical audits, stress testing, breach scenario modeling, and white hat (controlled) hacking.
Step #6: Keep Healthcare Systems Upgraded
Perform a technology audit and identify outdated medical applications, including medical device operating systems. Create and follow a strategy for upgrading obsolete healthcare systems, keeping cybersecurity as one of the highest priorities. Numerous modern health-tech technologies can also be considered for implementation: AR/VR, intelligent AI-driven components, migration of onsite health IT systems to cloud platforms, and more.
Step #7: Partner with Trusted Vendors
It’s okay that healthcare organizations often work with third-party vendors and partners. However, it’s necessary to select HIPAA-compliant vendors that have a strong security approach and follow appropriate protocols to protect client data. If you are looking for a reliable tech partner for IT management, custom medical software development, and maintenance, you can rely on TATEEDA GLOBAL.
To let our experience speak for itself, please check out our health-tech project portfolio for more details:
Delivered Healthcare Software Portfolio
The leading American healthcare companies benefit from working with us.
How Can TATEEDA GLOBAL Help You Build Secure Healthcare Systems?
All of the projects in which we participate incorporate a deep cybersecurity culture and specific methodology. Obeying the security principles explained in HIPAA and other crucial cybersecurity regulations is not a one-time effort, but a baseline process integrated into every team action and Agile development concept we use.
We can help you…
- Create role-based mobile and web applications with multi-factor user authorization procedures, as we did for AYA Healthcare.
- Build pharmaceutical web-access portals and back-end systems with secure database functionality, like SCRx Pharmacy.
- Implement optimized, protected client-server connection and data exchange between components of medical IoT systems like VentriLink.
- Create a lab device automation system with embedded programming and an integrated dashboard system for technicians, like this project.
FAQ: Data Protection in Healthcare
What are the biggest threats to data in healthcare?
The human factor is one of the most dangerous threats in healthcare IT, because many medical data breaches take place because of staff negligence. However, this problem is manageable. With the help of human-focused cybersecurity practices (passwords, activity monitoring, training, and so on), it’s possible to minimize healthcare data breaches and incidents.
How can you protect medical data?
Generally, you can keep PHI secure in your organization if you avoid these mistakes:
- Keeping legacy (obsolete) systems in operation without upgrades
- Hiring cheap IT vendors to save on IT security
- Ignoring cybersecurity threats and risks
- Avoiding staff training and failing to communicate with staff on security matters
- Not having cybersecurity products and procedures deployed in the organization.
Why is data security the biggest challenge for healthcare businesses?
Because one single mistake or omission can return at a truly huge cost.
If you want to discuss ways to improve your healthcare cybersecurity approach, please contact us and book a free call with one of our skilled engineers.









![Best AI Development Companies [USA] Title Image](https://tateeda.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/Best-AI-Development-Companies-for-the-United-States-1-2.jpg)
