EDI in Healthcare: Privacy with Less Paperwork

Anyone who has sought medical care for any purpose knows that scads of paperwork are generated with every case.
Not only does every medical visit involve stacks of forms full of fine-print paragraphs that are nearly impossible to read, but billing systems generate even more paper waste.
Those forms and documents pass through many hands, exposing patients’ private information and increasing the risk of human error.
Healthcare Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) technology ensures the security and privacy of electronic data transmission. It significantly reduces healthcare paperwork and the filing and storage nightmare that goes with it. Healthcare EDI also protects patient privacy and allows patients to retrieve and review their own medical records.
Equipping your clinic or practice with EDI software will dramatically improve your workflow, enrich the quality of care you are able to provide your patients, and increase patient loyalty.
In this article, we’ll talk about EDI technology as such, its basics, transactions, legal background, and popular types of EDI software, including common EDI tech applications in medical facilities and computer-aided systems across the US.
Moreover, you’ll understand how EDI works, and what aspects are to be taken into account when you build a new EDI-equipped system, and whether it’s possible to add EDI to your current healthcare software system.
Table of Contents
Healthcare EDI and HIPAA Compliance
Concerns about healthcare security and privacy are nothing new. In fact, they were addressed with legislation, long before the public worried about hackers and Internet data breaches. In 1991, the Workgroup for Electronic Data Interchange was created under President George H. W. Bush. The NPO was tasked with reducing healthcare costs in the United States. In 1996, as the electronic transmission of healthcare information increased, the group played a pivotal role in the enactment of the Healthcare Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
HIPAA’s primary objective was to institute national standards to protect patients from an invasion of privacy, a right guaranteed by the US Constitution’s 4th Amendment. HIPAA safeguards patients’ sensitive health data from being shared without the consent or knowledge of the patient. The HIPAA system assigns identifiers to professionals who have access to private health information, including insurance providers, clinicians, administrators, and anyone else privy to personal health details. The identifiers ensure that patient records are viewed only by individuals who have been authorized by the patient and are accessing their records under the protection of special electronic data interchange tools, preventing privacy leaks.
HIPAA includes an EDI Rule that obliges all healthcare-related entities in the US to enter their electronic data transmissions in compliance with a common EDI tech format. The “EDI rule” sets ANSI ASC X12 (X12) as the transmission protocol standard, providing a list of specific tech requirements that must be implemented by all covered organizations in their daily data operations.
If a healthcare provider or any other entity accessing medical records knowingly violates the EDI rules for HIPAA compliance, they risk having to pay considerable penalties, depending on the degree of negligence and the type of HIPAA violation. Fines can be as high as $10,000-50,000 USD per violation. In some cases, a criminal investigation and prosecution are even possible. The HHS Office for Civil rights is charged with enforcing EDI compliance in the healthcare industry.
Healthcare Electronic Data Interchange enhances compliance with HIPAA guidelines by streamlining the handling of medical records and other sensitive documents. It reduces the exposure of private patient records to unauthorized entities while increasing the speed, accuracy, and efficiency of record-keeping. HIPAA EDI software solutions are both advantageous and required by law in the US.

What is Healthcare EDI?
People everywhere have grown accustomed to having instantaneous access to data, especially when it comes to personal records.
With today’s technology, there is no excuse for keeping them waiting. Yet the healthcare sector has lagged behind in adopting technology to organize, store and administer patient records. HIPAA-regulated EDI transactions ensure that standardized medical documents are accessible and manageable via certified software systems.
In addition to establishing standards for protecting patient privacy, HIPAA acknowledges the legally enforceable right of patients to request and gain access to their own healthcare records. For most of us, that means immediate access, without having to wait for days or weeks.
EDI transactions replace traditional paper documents and unprotected computer-generated text emails, PDF files, fax, USB drives, and other vulnerable documents. Paper-based transactions are slow and can never guarantee instant access, and computer communications may expose your sensitive records to the risks of data breaches, tampering, or loss.
Along with establishing a common structured format for sensitive data, EDI allows for the unified and consistent transmission of medical records across a multitude of data systems used by various healthcare-related entities and patients across the USA.
Prior to the acceptance of EDI standards in 1996, there were 400+ electronic formats in use for transmitting healthcare claims, resulting in poor interoperability of different systems and higher costs of IT services due to persistent data conversion errors.
To meet HIPAA standards for access and privacy, insurers and healthcare providers are turning to EDI solutions for secure and private electronic transmission of patient records. HIPAA-regulated EDI transactions also make it easier for medical professionals to share vital patient information, to prevent misdiagnosis, incompatible medications, ineffective treatments, and other vital errors that endanger patient health.
How Does EDI in Healthcare Work?
The medical EDI X12 standard works as a bridge language between the computer systems of different US healthcare organizations, allowing for smooth automatic communications among them.
Additionally, HIPAA EDI technology creates a layer of protection for data transmissions between different electronic systems and healthcare applications to keep patient data confidential.
Thanks to secure healthcare EDI transactions:
- Care providers can collaborate and securely exchange medical information.
- Communications are protected from interception and deciphering, unlike emails or unprotected web connections.
- Sensitive healthcare documents and records are readily accessible to patients, administrators, and care providers, without software incompatibility issues.
The EDI-Standardized Transaction Process
The X12 EDI ANSI standard is generated by X12, a non-profit organization that develops cross-industry standards accredited by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). The standards are widely used to build EDI systems in the USA.
The EDI transaction process for healthcare and other EDI supported industries follows a series of steps:
Step 1: Prepare data to be transmitted
Create a document or a file with a correctly organized data structure. This can be accomplished in several ways:
- Manual data entry via electronic forms
- Export records from spreadsheets
- Extract objects from healthcare databases
- Use special computer applications to auto-create EDI-compliant documents
- Implement custom healthcare EDI software solutions,
Step 2: Format the document to match EDI X12 requirements
Electronic data must be translated into the EDI standard message format featuring specific data segments and elements. Typical EDI files in healthcare consist of segment names, segment/element separators, data elements, composite elements (data groups), and some other essential syntax units. This task can be carried out with the help of software supporting HIPAA EDI formats or done manually by a programmer.
Step 3: Transmit your EDI-formatted healthcare document to an authorized receiver
Once the documents have undergone EDI formatting, it’s time to establish a connection and send them to your EDI trading partner using one of several available EDI communication channels:
- Direct EDI (Point-to-Point, P2P)
- Value-Added Networks (VANs) and EDI Network Services Providers
- AS2/AS4 protocols
- FTP/VPN, FTPS, SFTP
- Web-based EDI
- Mobile EDI
- Cloud EDI
- EDI Software
- Some combination of solutions listed above
Modern EDI-compliant software products allow authorized users to seamlessly execute business operations in a few clicks.
Other EDI Standards
The X12 standard is not the only EDI standard available. The UN-backed Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce, and Transport (EDIFACT) protocol is an alternative to X12 and is recognized internationally, used predominantly outside of North America.
EDIFACT was developed under UN supervision and is widely used in Europe and Asia for a variety of business applications. However, only the EDI X12 standard works for HIPAA-compliant documents. EDIFACT is not compatible with HIPAA requirements.
Types of healthcare EDI transactions include:
- EDI (837): Health Care Claim Transaction Set
- EDI (997): Functional Acknowledgement Transaction Set
- EDI (270/271): Healthcare Eligibility and Benefits Inquiry/Response
- EDI (276/277): Healthcare Claim Status Inquiry/Response
- EDI (278): Healthcare Service Information Authorization and Referral Request
- EDI (278N): Hospital Admission Notification
- EDI (835): Electronic Healthcare Remittance Advice (ERA) Transaction Set
Advantages of implementation EDI in Healthcare
Healthcare EDI transaction software is transforming the healthcare business by reducing tedious paperwork and costs, enabling healthcare providers to spend less time and money on administration, and more time focusing on patient health.
Benefits of implementation EDI in healthcare include:
- Paperless transactions: EDI lets healthcare go green by minimizing the use of paper, reducing deforestation and CO2 emissions.
- Standardized procedures: Standard EDI formats dramatically improve efficiency, simplifying healthcare management, reducing costs, and improving the quality of patient care.
- Enhanced security: Data transmissions between providers, insurers, and patients remain secure and private with EDI software solutions, ensuring HIPAA compliance.
- Improved accuracy: Healthcare EDI solutions help speed up transactions while eliminating human error, including keying errors, lost documents, incorrect entries, and other errors that slow down and stall data transmission. If a healthcare provider implements custom healthcare EDI software, they not only ensure that the documentation process is streamlined, but they also eliminate the potential for human error.
- Optimized costs: Hospitals, clinics, and private practices can dramatically lower the cost of processing and filing healthcare documents while reducing the time it takes for document processing.
EDI solutions put everyone on the same page, so that healthcare providers are able to prioritize patient care. At the same time, patients are able to access EDI records and co-manage their healthcare needs. Custom EDI software is a win-win solution for everyone, bringing today’s healthcare systems up to speed to meet the demands of the 21st Century.
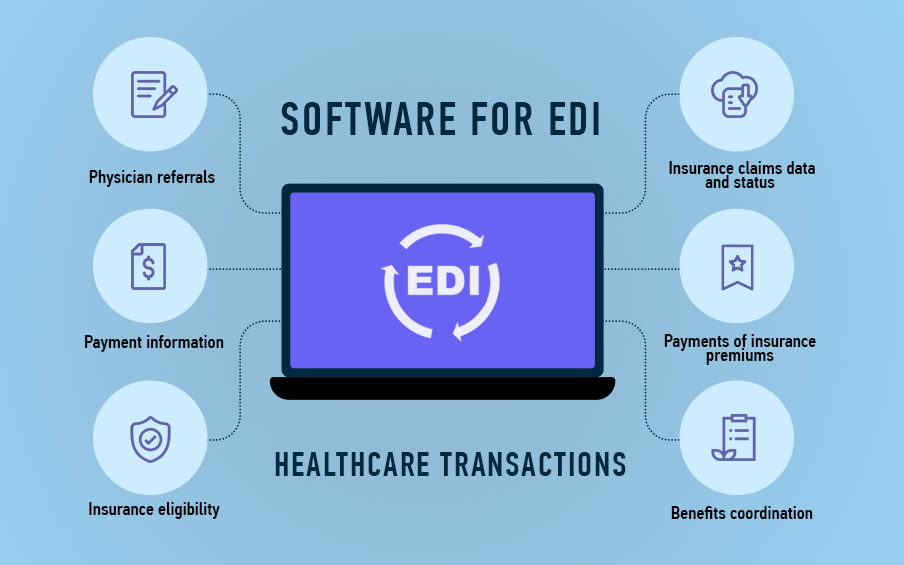
Development Guidelines for EDI Healthcare Software
Healthcare software development must take into account EDI standards for HIPAA compliance. In addition to safeguarding sensitive information about patient health, EDI transactions are used for:
- Physician referrals
- Payment information
- Insurance eligibility
- Data and status of Insurance claims
- Insurance premium payments
- Benefits coordination
With so many moving parts for each patient visit and treatment, it makes sense to adopt a software system that can manage all aspects of the patient journey, from their first encounter with the system through their final payments and beyond.
Types of EDI Software: What EDI Solutions Are Popular With Healthcare Providers?
There are numerous different software solutions that use EDI-standardized transaction sets.
The most common EDI software systems include:
- Hospital Information System (HIS): This all-encompassing solution helps hospitals and clinics to administer different aspects of their daily activities, including patient data, medication plans, internal inventory, medical appointments, medical billing data, and other data related to daily operations. HIS systems are powerful enough to handle different types of incoming and outbound EDI requests and documents, seamlessly integrating them into the hospital’s daily workflow.
- Patient portals: Mobile and web-based EDI-supporting systems enable patients to access their medical records, including diagnosis, treatment, online prescription data, billing for healthcare services, remote notifications, and other relevant information.
- Electronic Health Record (EHR): EHR is a systematized registry of patient statistics and health data that can be shared across different authorized healthcare providers and hospital subdivisions. EHR data includes demographics, medical history, allergies, immunization profiles, laboratory test results, billing inquiries, and other information necessary to provide a holistic profile of each patient.
- Medical practice apps: Mobile applications and other mobile solutions allow healthcare providers to instantly and securely access and review patient health data and insurance information.
- Patient relationship management (PRM): PRM software helps healthcare providers to adopt a business-like approach to the patient care journey. PRM enables healthcare providers to facilitate and analyze the patient experience at every stage, from referral to treatment. PRM involves a considerable number of EDI-protected communications and documents that help to map out each patient’s individual journey.
Components of HIPAA Compliant EDI Healthcare Software
Custom EDI solutions have four essential EDI system components:
- Device(s) involved in the data transmission process (smartphones, PCs, workstations, network devices, tablets, etc.)
- An application that formats the data according to HIPAA EDI requirements (supporting X12 protocol.)
- A secure and stable connection between the sender and the recipient, established through one of the allowed environments.
- Authorized users qualified to operate and interpret the medical and business data being sent and received within the EDI system.
Developing HIPAA compliant custom medical software with EDI technology
Not all available healthcare software systems meet the highest HIPAA standards, and using them can lead to Protected Health Information (PHI) violations, making users liable and subjecting them to damages and penalties.
Sometimes, legacy software systems do not support the latest version of EDI standards. Those medical systems can be upgraded and integrated with EDI-supporting modules.
Whether you’re developing custom healthcare EDI software or implementing EDI into existing systems, it’s important to adhere to certain requirements for secure operations of PHI:
- User access. Distinct user groups and types, including administrators, care providers, support staff and patients, are assigned a hierarchy of rights and business processes. Protected user interfaces are designed to authorize or deny access to EDI files, documents, and other patient data.
- System architecture. Appropriate system architecture allows users to format, store, generate, change, save and retrieve EDI information in errorless, safe, and consistent ways.
- Communication. The communication infrastructure should be supported with sufficient encryption types.
- Security. Hackerproof user identification systems including passwords, PINs, biometrics, smart keys, and other secure user IDs should be implemented, along with emergency access and data restoration procedures, automatic sign-off, security alerts, and other precautions.
Customized EDI Software Solutions from TATEEDA
Choosing or building a healthcare EDI software solution capable of covering all the needs and requirements of modern healthcare requires expertise in HIPAA EDI standards and knowledge of medical software architecture. TATEEDA is a reliable partner that can help you build a HIPAA compliant custom healthcare EDI software system.
We can also implement EDI support for your existing software system, or consider re-engineering other types of legacy systems.
We are experts in conceptualizing and developing full-cycle/full-stack medical software systems that support EDI communications, such as:
- Pharmacy inventory and delivery management platforms: medication delivery and documentation management, integration with shipping providers, delivery tracking, etc.
- Physician and nurse appointment scheduling software development: scheduling and tracking of medical personnel, medication plans, appointments, time entries, routes, and other relevant information.
- Hospital Management Systems with multiple modules and powerful features (Check our Complete Guide to Developing Hospital Management Software)
- Lab Information Management System (LIMS): software modules for lab automation, optimization of lab procedures, multi-equipment use, reporting, etc.
- Patient portal app/web solutions: protected mobile access to personal health data profiles, nearby medical office lookup, notifications, etc.
- EDI for healthcare suppliers: medical inventory management and tracking, integration with billing solutions, etc.
Other services provided by TATEEDA include project-based staff augmentation, outstaffing services, and on-demand legacy software modernization.
Do you have a software solution idea for your healthcare facility or organization? Please get in touch with us for a free consultation!
Why Build Custom EDI Healthtech Solutions with TATEEDA?
Whether you are a small private practice or clinic, or a large healthcare system that serves thousands of patients, TATEEDA can design and develop a custom EDI software solution to meet your unique needs. TATEEDA’s EDI software is safe, secure and HIPAA compliant, to protect you and your patients from data privacy breaches.
Reduce costs and paperwork, increase accuracy and efficiency, and bring your organization up to speed to meet today’s demands for access, privacy, speed, and compliance in healthcare management.
Contact TATEEDA today for a consultation and free estimate!









![Best AI Development Companies [USA] Title Image](https://tateeda.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/Best-AI-Development-Companies-for-the-United-States-1-2.jpg)
