Top 4 Telemedicine Integration Strategies: Guidance from Healthcare IT Consultants

In this article, you’ll uncover telemedicine integration strategies, address telehealth implementation challenges, and explore proven telemedical solutions to enhance health service delivery, including the best cost of telehealth system implementation.
The U.S. healthcare is bracing for a critical shortage—by 2025, rural communities could lack approximately 20K primary care doctors. This scarcity amplifies the struggles underserved regions face, where recruiting and retaining healthcare professionals—such as primary care physicians, nurse practitioners, mental health specialists, and pediatricians—remains an uphill battle.
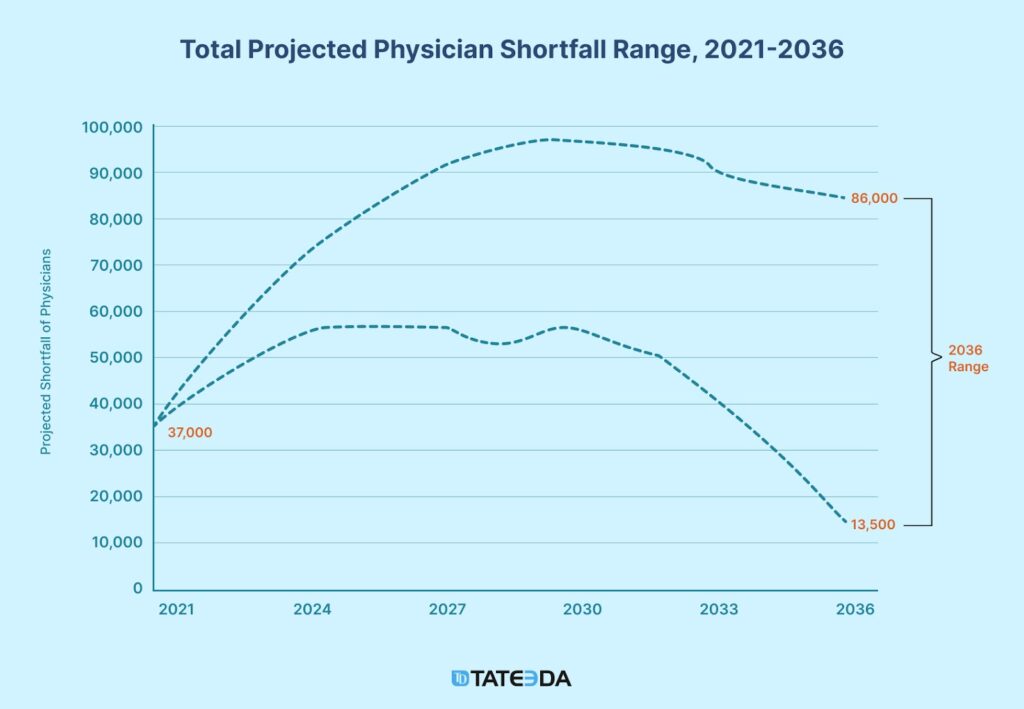
Simultaneously, the cost of medical care in the United States continues its steady climb, with annual spending projected to rise by 5.4% through 2028. These factors converge to create an accessibility crisis, leaving millions without consistent medical support.
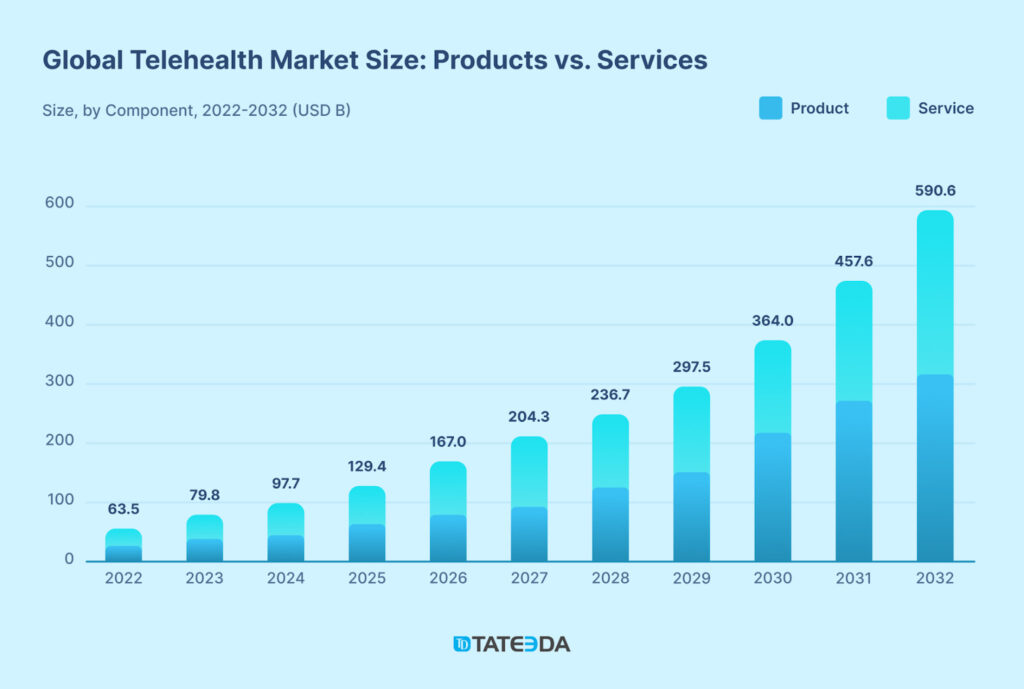
Similar critical situations are emerging in many global locations and are not exclusive to the U.S. (related to the global aging population trend and other transnational factors). The chart below illustrates how telehealth integration strategies are gaining traction, attracting steadily increasing investment volumes, and are projected to garner even more trust as the shortage of medical professionals deepens.
Learn more: ➡️ AI Assistant Development Services
How can a telehealth integration strategy help mitigate these issues while keeping the entire system financially afloat?
Custom telemedicine solutions offer a lifeline in these negative conditions, providing a ray of hope amidst the otherwise dark scenarios that underserved regions are poised to face, including increased mortality rates and local populations suffering with no professional medical help.
These solutions encompass a variety of applications, including:
- Virtual consultation platforms for real-time doctor-patient interactions
- Remote patient monitoring systems for chronic disease management
- Patient portals for accessing medical records, payments, test results, and secure communication with healthcare providers
- Telehealth platforms integrated with electronic health records (EHRs)
- Mobile apps for appointment scheduling and medication reminders
- Specialty telehealth services like telepsychiatry and teledermatology.
Implementing telehealth using advanced communication technologies, it empowers physicians to connect with their patients in real time, no matter the distance, even when patients face medical conditions like immobility.
This method has proven very promising, as it not only bridges the gap between rural and urban healthcare access but also reduces providers’ costs by preventing treatment-related illnesses.
For example, applying emerging telemedicine solution trends has successfully lowered hospital readmission rates by as much as 20% and enabled early detection of chronic conditions through remote monitoring systems.
Notably, only 25% of the global physician workforce serves 50% of the rural population, and in the United States, researchers have found that less than 12% of physicians practice in rural areas, highlighting the urgent need for scalable telemedicine solutions.
| Why is TATEEDA well-suited to discuss telehealth implementation challenges and solutions? We are headquartered in the U.S. (San Diego, CA) and have helped many local companies build their telehealth solutions. One of these solutions was VentriLink, an ECG-monitoring application that monitors and records cardiac rhythms in remote patients in real time. This included automation and various tools for cardiologists, such as detecting dangerous ECG patterns and sending alerts to healthcare providers. Do you have a telehealth solution software in mind for the United States market? We can help! Our local IT project experts are available for personalized communication and HIPAA-compliant health-tech consulting. |
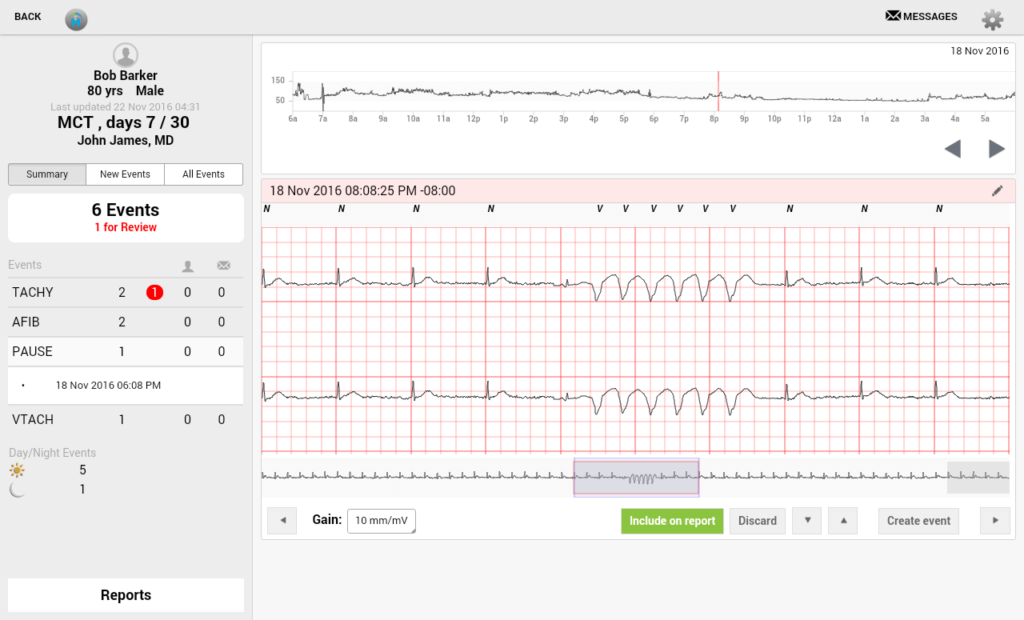
However, implementing telehealth systems comes with its own set of telehealth implementation challenges and solutions, from ensuring compliance with stringent regulations (HIPAA, CCPA, GDPR, FDA, and more) to overcoming technological and logistical barriers, especially in areas with limited infrastructure.
In the sections ahead, we’ll explore actionable telehealth integration strategies designed to address these obstacles. Whether you’re a healthcare leader, IT consultant, or medical practitioner, this guide provides the insights needed to build effective, sustainable telemedicine solutions.
Table of Contents
The Top 7 Telehealth Implementation Challenges in 2025
Implementing AI-aided telehealth systems holds tremendous potential for enhancing healthcare accessibility and medical service efficiency, yet the process is fraught with multifaceted obstacles.
Although each of these challenges has an appropriate telehealth integration strategy for countering, implementation requires careful planning and technical expertise. Key changes under the CARES Act include:
- Expansion of approved telehealth platforms, such as FaceTime and Zoom, to enable more versatile communication.
- Authorization of audio-only consultations, providing greater inclusivity for patients with limited access to video or audio technology.
- Permission for cross-state telehealth services to address critical shortages in healthcare providers, particularly in distant and underserved rural areas.
Despite these tech advances, healthcare organizations continue to face significant telehealth implementation challenges and solutions must address them comprehensively. Below, we delve into the primary barriers to telehealth implementation, including raising the cost of telehealth implementation, and offer actionable insights to overcome them.
1. Telemedicine Regulatory Compliance ??
Adhering to stringent regulations, including HIPAA, CCPA, GDPR, and FDA guidelines, remains a cornerstone challenge in telehealth implementation projects. Organizations must deploy solutions that come with proper data encryption, secure communication protocols, and rigorous patient privacy frameworks to ensure sufficient regulatory alignment of their telemedicine tools. Non-compliance risks not only financial penalties but also irrevocable reputational damage, followed by potential lawsuits from patients if data breaches or privacy leaks occur.

In 2024 alone, 13 data breaches involving over 1 million healthcare records were reported, including the largest healthcare data breach in history, which exposed the records of 100 million individuals.
These breaches compromised 146 million records, representing 42% of the U.S. population. Improperly designed telehealth implementations were also implicated, underscoring the critical importance of well-architected solutions to prevent such outcomes and mitigate the risks of future breaches.
2. Technological Barriers for Telehealth ??
Effective telehealth demands a resilient technological ecosystem encompassing high-speed internet, secure software infrastructure, and interoperable medical devices. Rural and underserved regions—where telehealth can make the most impact—often grapple with inadequate broadband infrastructure, amplifying implementation difficulties.
By prioritizing lightweight, resource-efficient software platforms, organizations can better serve these communities without compromising the quality of communications and medical care.
“That’s why it makes sense to design or utilize telehealth solutions that optimize scarce internet bandwidth and limited resources, minimizing lags and ensuring smooth operation even in low-connectivity environments. ”
— Andrew G., TATEEDA’s Health Tech Architect
3. Provider and Patient Adoption ??
Telehealth adoption hinges on overcoming resistance from both providers and patients. Low digital literacy, skepticism about remote care efficacy, and entrenched workflows impede telemedical software acceptance. Comprehensive training initiatives for both healthcare providers and their patients and the deployment of intuitive, user-centric platforms are critical to mitigating these challenges.
Additionally, custom healthcare software developers must exhibit advanced proficiency in crafting user-friendly and minimalistic user interfaces that suit patients of all skill levels and ages, while employing cloud technologies to run custom backend programming mechanisms and retrieve necessary medical data quickly and cost-efficiently.

4. Integration with Existing Systems ??️
Flawless interoperability between telehealth platforms and core healthcare systems, such as electronic health records (EHRs) and custom practice management software, is essential for simultaneous recording and updating of PHI (Protected Health Information), ensuring data consistency across platforms. Standards like HL7 FHIR for medical software integration facilitate secure and structured data exchange between systems, ensuring that patient information is consistently and safely shared across platforms. Achieving this integration without disrupting existing workflows requires advanced interface engineering and thorough systems testing.
5. Financial Constraints ??
Deploying telehealth solutions necessitates significant financial outlays for technology acquisition, staff training, and ongoing operational costs. While custom telehealth solutions require substantial investments, there are off-the-shelf alternatives—some even free. However, these options may lack full HIPAA compliance and can introduce reliability concerns, such as security loopholes, that custom solutions are designed to avoid. Strategic investment planning and phased rollouts can help mitigate these burdens.
6. Legal and Ethical Challenges ⚖️?
Recent legislative changes, including the CARES Act, have alleviated some legal hurdles, such as allowing cross-state telehealth services and expanding the use of audio-only platforms. However, complex legal frameworks (like HIPAA) still present roadblocks, including cross-state licensing requirements and liability concerns. Ethical issues, such as equitable access and data sovereignty, further complicate telehealth deployment. Proactive engagement with legal counsel and policymakers is essential to navigate these complexities.
7. Quality Assurance and Monitoring ?✅
Ensuring consistent care quality through telehealth requires well-engineered monitoring systems, error-detection mechanisms, and stringent code performance benchmarks. Regular source audits, analytics-driven refactoring efforts, and iterative feature improvements are vital for maintaining telehealth service excellence and patient trust.
“The key to unlocking telehealth’s full potential is combining strategies like phased rollouts, seamless interoperability powered by APIs and HL7 standards, and leveraging cutting-edge tools like AI-powered diagnostic platforms and secure healthcare cloud infrastructures, all while maintaining deep expertise in compliance and system integration.”
– Slava K., TATEEDA’s CEO
Telehealth Integration Strategy #1: Get a Pro-grade Medical Solution Instead of Generic Software
Let’s start with one of the questions that we at TATEEDA are often asked by our clients and prospects:
Can Skype or Google Meet be used as telehealth solutions?
No, we do not recommend using them for telemedicine. This is because software packages like Skype, Google Meet, Viber, and similar ordinary teleconferencing platforms can certainly connect doctors and patients but fall short of meeting professional telehealth system requirements.
They often lack compliance with regulations like HIPAA, posing risks to patient data, and do not offer essential healthcare-specific features like EHR integration, scheduling, or remote patient monitoring.
Additionally, these systems may not provide the security, encryption, or customizability required for medical use. While they can be helpful in emergencies, purpose-built telehealth platforms are far better suited to meet the needs of healthcare providers and patients.
What professional off-the-shelf telehealth products are currently available?
While ordinary teleconferencing platforms like Skype and Google Meet may appear to reduce the cost of telehealth implementation due to their low or no upfront expenses, relying on these tools can lead to significant risks…

If a data breach occurs and patient information is exposed, healthcare organizations could face severe penalties under HIPAA regulations. The fines can reach up to $1.5 million per violation—enough to make even the healthiest financial statements look unwell. That’s why we never advise telemedicine integration strategies that rely on free or non-medical teleconferencing products.
To mitigate such risks, it is strongly recommended to adopt at least off-the-shelf telehealth products, which provide the necessary compliance and security features. The table below outlines the differences between ordinary platforms and professional telehealth solutions:
| ❌ Ordinary Teleconferencing | ✅ Professional Telehealth Products |
| Skype: Lacks HIPAA compliance, robust encryption, audit logs, and secure storage for patient data. | Teladoc Health: Provides virtual healthcare with HIPAA compliance, integrated mental health services, chronic condition management, and support for second medical opinions. |
| Google Meet: Designed for general use; lacks built-in HIPAA compliance features, advanced access controls, and secure data handling protocols. | Doxy.me: A secure, HIPAA-compliant telehealth platform offering video consultations with encryption and ease of use for providers and patients. |
| Viber: Primarily a messaging app; lacks healthcare-specific features, encrypted data handling for PHI, and audit trails necessary for compliance. | SimplePractice: Tailored for mental health professionals, featuring HIPAA-compliant video sessions, secure documentation, and robust appointment scheduling tools. |
| WhatsApp: While encrypted, it lacks HIPAA-compliant features such as data auditing and secure storage tailored for healthcare. | American Well: Offers HIPAA-compliant telehealth solutions with customizable services for healthcare systems, employers, and insurers. |
| FaceTime: General-purpose video calling; lacks audit trails, advanced encryption standards, and secure data storage needed for HIPAA compliance. | HealthTap: Provides HIPAA-compliant virtual care with AI-driven symptom checks, 24/7 primary care access, and comprehensive health management features. |
| Zoom (standard): Regular accounts are not HIPAA-compliant and do not include advanced security configurations required for professional healthcare use. | CareCloud Live: A telemedicine solution integrated with EHR systems, enabling HIPAA-compliant virtual consultations and optimized clinical workflows. |

Not Sure Which Telemedicine Integration Strategies to Choose?
Since 2013, we’ve been helping U.S. companies and are ready to provide IT consulting on the best methods and costs.
Telemedicine Integration Strategy #2: Develop a Custom Medical Software Setup
In our opinion as health IT consultants, the best approach to implementing telehealth in medical practice is to create a custom proprietary product or use deeply configurable pro-grade platforms. Customizing telehealth functionalities will help you align with your business workflows, including the protocols followed by your representatives and physicians, as well as uphold the best ethics of communication with your patients (this involves using remote patient feedback to polish your final applications.)
“Custom telehealth solutions or highly configurable pro-grade platforms go beyond just the tech—they’re about creating tools that fit your team like a glove. One of our clients reported that after implementing a better-customized solution, over 80% of their patients expressed satisfaction with telehealth communication compared to just 35% before.
Additionally, 90% of their patients found the mobile apps convenient and reported no negative experiences. It’s about streamlining workflows for doctors and staff while ensuring patient interactions remain personal and ethical. That’s how you make virtual care feel as connected as in-person visits.”— Anastasia M., TATEEDA’s Tech Lead
Learn more: ➡️ Top 10+ Healthcare Mobile App Trends Shaping the Industry
What sets ordinary teleconferencing software apart from professional telehealth systems?
Of course, the cost of implementing telemedicine rises if you opt for a custom medical software solution. However, the price is not excessive when compared to the wealth of opportunities this decision provides. This table clearly demonstrates how regular teleconferencing platforms differ from purpose-built telehealth solutions and their specialized medical features.
| Aspect | Ordinary Teleconferencing | Purpose-Built Telehealth Platforms |
| Compliance | May lack full compliance with healthcare regulations like HIPAA, risking patient data privacy. | Fully compliant with regulations (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR) to ensure patient privacy and data security. |
| Healthcare Features | Limited to basic video conferencing; lacks EHR integration, scheduling, billing, and patient monitoring tools. | Designed for healthcare needs, offering integrated EHR, appointment management, billing, and remote patient monitoring. |
| Security | Provides encryption but may lack end-to-end security or audit trails needed for healthcare data handling. | Offers advanced encryption, audit logs, and secure communication protocols tailored for sensitive medical information. |
| Customizability | General-purpose design; lacks flexibility to meet the specific needs of healthcare workflows. | Highly customizable to support unique provider workflows and patient requirements. |
| Scalability | Suitable for small-scale use; struggles to support large healthcare organizations or specialized services. | Scalable for organizations of any size, accommodating high patient volumes and specialized telemedicine services. |
| Trust and Reliability | Perceived as a temporary or emergency solution; may not inspire long-term trust among patients and providers. | Built for reliability with features like system uptime guarantees, redundancy, and a healthcare-focused design. |
| Data Interoperability | Cannot integrate with other medical systems, making data transfer manual and error-prone. | Enables seamless data exchange with standards like HL7 FHIR, ensuring smooth interoperability across healthcare platforms. |
| Patient Engagement | Lacks features for engaging patients beyond calls, such as automated reminders or post-consultation follow-ups. | Includes tools like appointment reminders, secure messaging, and follow-up care management to improve patient outcomes. |
Telehealth Integration Strategy #3: Design Easy, Inclusive, and Lightweight UI
This strategic action ranks third on the list but is no less impactful in its significance, and here’s why…
Imagine a disabled senior patient, Mrs. Thompson, who relies on telehealth for her regular checkups. She receives a link to her session but finds the platform’s interface overly complex, with tiny icons, unclear labels, and confusing navigation—a significant challenge for someone with mild vision impairment.
Logging in takes multiple frustrating steps, and starting the video call brings a technical error she cannot easily resolve. Essential features, like medication management, are hidden in submenus, leaving her unable to refill prescriptions without help from her caregiver.
Instead of simplifying care, the poorly designed interface creates barriers, leaving Mrs. Thompson stressed and hesitant to rely on telehealth in the future.
Recommendations for creating accessible and inclusive telehealth interfaces:
- Simplify Navigation: Use straightforward, logically structured menus with clearly labeled sections. Ensure key features like appointment booking and prescription management are vivid and accessible without confusion or unnecessary effort. For instance, a “one-click to book” button can reduce user frustration. Imagine the relief of skipping endless submenus!
- Optimize for Accessibility: Incorporate design elements such as high-contrast large fonts, adjustable text sizes, and full compatibility with assistive technologies, including screen readers and magnifiers, to support users with vision impairments or other accessibility needs. Think of it as giving every user a personalized lens for navigating your platform effortlessly.
- Reduce Complexity: Minimize extra steps for essential actions. Simplify login processes and provide one-click functionality for critical features like starting video calls to create a seamless and frustration-free experience. After all, no one wants their medical appointment delayed by a 10-step verification dance!
- Provide Clear Error Guidance: Craft error messages in simple, actionable language and complement them with visual aids or tooltips to guide users toward quick and effective solutions. “Oops! Your mic is muted. Click the mic icon to unmute” is far more helpful than technical jargon.
- Test with Diverse User Groups: Conduct thorough usability testing that includes older adults and individuals with a range of disabilities to uncover potential barriers and refine the interface accordingly. A 75-year-old grandparent navigating your platform like a pro? That’s the goal.
- Offer Multi-Language Support: Integrate multiple language options and localized content to support users from various linguistic and cultural backgrounds, ensuring broad accessibility in the United States and even globally. Think of it as opening your digital doors to a global village.
- Implement Voice Controls: Add voice-activated commands to enable hands-free navigation and task completion, particularly benefiting users with physical limitations or dexterity challenges. Picture a patient saying, “Book an appointment with Dr. Smith,” and seeing it done instantly—that’s the power of voice integration.

Telehealth Integration Strategy #4: Create a Convenient Patient Access Portal
It doesn’t matter if you choose to build a custom telehealth solution or use an off-the-shelf product—you need to design and develop a patient portal that ensures exceptional accessibility and leaves your patients satisfied. A well-designed portal minimizes stress in users by reducing the time they spend booking appointments or paying medical bills.
Recommendations for Creating a Convenient Patient Access Portal
- Prioritize Clarity and Inclusivity: Ensure the portal is easy to navigate, with simple language, intuitive design, and accessibility features like adjustable text sizes, high contrast modes, and compatibility with screen readers. Imagine a visually impaired patient effortlessly using a portal with clear navigation, readable fonts, and voice guidance—such thoughtful features can transform their experience and make accessing care stress-free. For instance, include features such as a streamlined homepage with large, clearly labeled buttons for key actions like scheduling and billing. Consider leveraging tools or frameworks like Material Design components or Bootstrap to simplify implementation and enhance accessibility. Successful examples include portals that offer visual progress indicators during multi-step tasks and responsive layouts that adjust seamlessly across devices.
- Choose a Platform That Supports Integration: Confirm that the product or platform you select allows seamless integration of custom patient portals, ensuring smooth interoperability with your existing telehealth system. Specify interoperability standards like HL7 FHIR or SMART on FHIR to guide your integration choices and ensure compatibility across platforms. Additionally, ensure the portal supports multiple payment options and integrates with reliable payment gateways, allowing patients to easily settle medical bills through credit cards, digital wallets, or other preferred methods. Or perhaps, you could enable a BNPL (Buy Now, Pay Later) model in healthcare to let your patients pay their bills in portions? Who knows, it might just make paying for healthcare feel a bit less daunting!
- Engage Professionals for Development: Work with experienced developers to create a portal that guarantees usability and integrates flawlessly with other system components, including patient databases and web-based platforms. Look for developers with certifications in relevant technologies, such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and frontend frameworks like Angular and Vue.js for web-based interfaces, and proven experience in building healthcare systems compliant with regulations like HIPAA. This ensures they can handle the specific technical and security requirements of your platform.
- Reflect Your Brand Identity: Incorporate vivid logos, color schemes, and branding elements that represent your medical center or organization, reinforcing trust and familiarity with your patients. For inspiration, consider platforms like MyChart, which effectively uses clean layouts and cohesive branding to maintain a professional yet approachable image.
- Balance Security and Simplicity: Implement robust authorization and protection measures to secure patient data while keeping the portal user-friendly. Employ two-factor authentication methods like SMS-based codes or biometric verification to enhance security without burdening users. Integrate CAPTCHA tools to deter unauthorized access and encrypt sensitive data to ensure HIPAA compliance. Additionally, use real-time system monitoring to detect and address security breaches promptly. Strive to maintain a balance between strong protection and ease of use, supporting inclusivity and accessibility for all users.
Case Study: Developing a Patient Payment Portal
Our team at TATEEDA collaborated with a U.S.-based medical provider to design a secure, web-based Patient Payment Portal tailored to streamline healthcare payments. Built using Angular for the frontend, .NET for the backend, and SQL Server for database management, this platform integrates advanced payment gateways like Spreedly and utilizes SSL encryption to safeguard sensitive data.
Beyond simplifying transactions, it empowers patients with tools to manage their finances effectively while adhering to strict regulatory standards, ensuring both compliance and ease of use.
- Payment Solutions: Supports online payments through credit cards, ACH, and e-checks with customizable one-time or recurring options.
- Flexible Payment Plans: Offers autopay and tailored installment options, reducing late payments by 15%.
- Educational Tools: Helps patients understand bills, insurance, and payment options, increasing transparency for accurate implementation of telemedicine.
- Secure Account Access: 24/7 access to invoices, balance tracking, and history with SSL encryption and two-factor authentication.
- Operational Improvements: Achieved a 30% reduction in failed payments and a 40% decrease in support requests while cutting processing times by 50%.
What about Telehealth Implementation Cost?
The cost of implementing telehealth fluctuates widely based on the solution’s scope and tech stack. Key pricing variables include the major choice between custom-built platforms or off-the-shelf products (the latter can be less expensive yet limited in their adjustment capabilities), the set of required software functionalities, and the level of integration with existing systems like electronic health records (EHRs), payment tools, and more. Regulatory compliance factors, including adherence to HIPAA, PCI, CCPA, and GDPR standards, further contribute to the overall cost of implementing telehealth in a medical organization.
For small-to-medium healthcare providers in the United States, telemedicine implementation costs typically range from $50,000 to $250,000. Enterprise-level solutions, involving advanced features such as AI-powered functions and analytics, blockchain-based data security, and multi-cloud infrastructure, can escalate beyond $1 million. Each of these investment tiers reflects varying levels of technological sophistication and operational capacity.
Cost Breakdown and Strategies for Optimization
| Expense Category | Estimated Cost Range | Optimization Strategies |
| Platform Development | $30,000–$150,000 | Use modular development and open-source frameworks to reduce custom coding needs. |
| Integration with EHRs | $10,000–$50,000 | Choose platforms supporting HL7 FHIR standards for seamless interoperability. |
| Security and Compliance | $10,000–$40,000 | Implement scalable encryption and compliance frameworks (e.g., HIPAA, PCI) upfront to avoid costly future retrofits. |
| Hardware and Infrastructure | $5,000–$30,000 | Utilize cloud-based services to minimize on-premises hardware costs. |
| Training and Support | $5,000–$20,000 | Provide focused training for staff using virtual modules to lower logistical expenses. |
Managing Costs Effectively
To manage telehealth implementation costs efficiently, consider starting with a minimum viable product (MVP) that addresses core functionalities, such as video consultations and basic patient record access. Gradually expand features like AI-driven diagnostics, patient portals, or advanced analytics as your organization’s needs evolve. Additionally, partnerships with established telehealth vendors can help mitigate initial setup expenses while ensuring a secure and compliant system.
The Final Word
As explored throughout this article, telehealth implementation is a multifaceted process shaped by numerous considerations, such as platform selection, required functionalities, regulatory compliance, and integration complexities. Whether opting for an off-the-shelf solution or developing a custom-built platform, costs vary widely depending on your organization’s size, technical needs, and strategic goals.
TATEEDA recognizes that managing telemedicine integration costs is a pivotal challenge for small-to-medium medical enterprises. Our multidisciplinary team—comprising seasoned frontend and backend developers, QA engineers, software architects, and project managers—is equipped to deliver secure, scalable, and regulation-compliant telehealth solutions. By aligning each project with your unique workflows, we ensure value-driven outcomes without compromising quality or efficiency.
Implementing telehealth doesn’t have to feel daunting or cost-prohibitive. TATEEDA is here to help you navigate the complexities, offering innovative, inclusive, and reliable telehealth systems tailored to your practice’s evolving needs.

Need Help with Telehealth Integration?
With a team of 100+ senior developers, we’re ready to accelerate your telehealth integration. Count on us for the best balance of speed, cost, and results.









![Best AI Development Companies [USA] Title Image](https://tateeda.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/Best-AI-Development-Companies-for-the-United-States-1-2.jpg)
