Medical Document Automation: How to Transition from the Excel Era to a Modern DMS

Efforts to achieve efficient document automation for healthcare organizations are often met with resistance from traditional workflows that still rely on paper-based document circulation or Excel-based systems. This also includes other electronic spreadsheets and generic electronic documents that are not fully suitable for managing medical records.
| ⚠️ If you require immediate assistance with adoption of document automation in healthcare, our engineers can build a system to meet these needs. CONTACT US FOR ASSISTANCE → |
Persistent use of these outdated methods frequently leads to operational inefficiencies, errors, and compliance issues. In this article, we delve into the critical significance of transitioning away from all Excel-based systems and adopting comprehensive medical document automation.
Research indicates that three significant challenges arise when medical documentation is conducted in spreadsheets and/or other nonspecific platforms:
- Inconsistent Nurse Documentation and Communication: The first issue revolves around inconsistent documentation and communication among nurses. This variability can lead to misunderstandings and gaps in patient care.
- Lack of a Centralized Care Overview: The absence of a centralized care overview within a patient’s electronic health record poses a substantial concern. This means that crucial information may not be readily accessible to the entire care team, potentially impacting decision-making and patient outcomes.
- Limited Interdisciplinary Communication: Another notable challenge is the infrequency of interdisciplinary communication. Collaboration between different healthcare professionals is vital for comprehensive patient care, and the current system often falls short in promoting effective cross-disciplinary exchanges.
| ? Remember that spreadsheet software, like MS Excel and similar products, isn’t designed for complex data-management tasks. Compatibility issues between versions and packages can result in data loss and reduced efficiency in medical paperwork. Additionally, Excel sheets (XLS) are constrained to 65,536 rows. |
Addressing these issues with the help of intelligent document processing in healthcare is essential to enhance the quality of medical documentation and, ultimately, improve patient care and outcomes.
? NOTE: To explore potential options for automating and digitizing your medical document workflows, please feel free to contact one of our experienced health-tech engineers:

Slava Khristich
Healthtech CTO
Based in San Diego, Slava knows how to design an efficient software solution for healthcare, including IoT, Cloud, and embedded systems.
Healthcare Sectors Prone to Inefficient Document Workflows
Before we explore potential methods of medical document automation, let’s examine some of the sectors most susceptible to redundant, outdated spreadsheet-based document operations:
? Clinical Trials: One significant challenge in collaborative clinical studies involves efficient, secure centralization of data. Separate study locations often employ different data collection systems, including Excel, Microsoft Access, and paper CRFs, leading to data silos. These discrepancies result in data fragmentation and add logistical complexity when centralizing and conducting statistical analyses.
? Medical Care Practices: Nurses and dedicated medical office workers manage a plethora of documents while frequently grappling with inefficiencies and tedium in manual processes. Clinics, ERs, and other medical practices commonly rely on Excel spreadsheets and similar data grids for tasks such as creating document indexes with shareable links; maintaining operational records; tracking working hours, shifts, and attendance; performing quick calculations; and more.
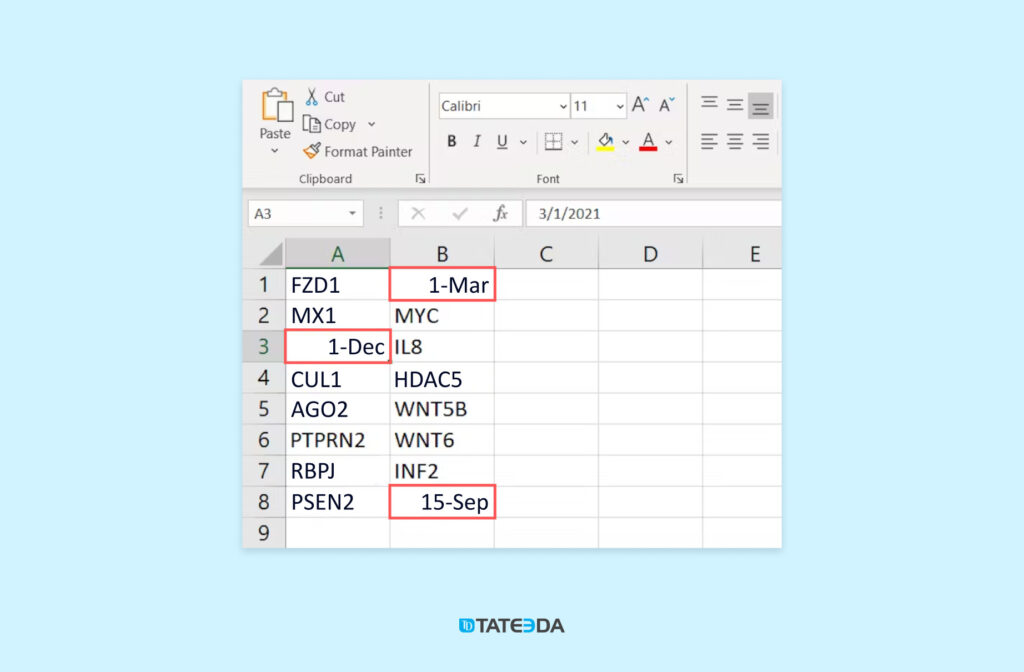
? Genetic Research: Opening an Excel file with default settings can inadvertently corrupt scientific data through autocorrection. Since 2004, Excel has been known to convert approximately 30 human gene and protein names into date formats, including MARCH1, SEPT1, Oct-4, jun, and others. In 2016, a study revealed that this problem affected both mid-tier and top-tier journals equally, highlighting the widespread lack of awareness among researchers and journals about Excel’s autocorrection issue and its prevention. In response to this report, the Human Gene Name Consortium, which is responsible for human gene nomenclature, took action, renaming problematic genes such as MARCH1 and SEPT1 to MARCHF1 and SEPTIN1, respectively, among other changes.
Which Medical Documents Can Be Automated?
While medical document automation software has evolved to generate intricate files with complex rules and detailed templates, applications have traditionally managed documents that only undergo minimal changes between iterations. It’s important to note that this type of software updates specific fields based upon preset rules and available information within the organization. These may include:
Table of Contents
Challenges with Excel in Medical Document Management
Spreadsheets have maintained a longstanding presence in the business world. Excel and other spreadsheet software have become so prevalent that many companies choose them over more robust database solutions, even though the latter could provide enhanced security and functionality.
While spreadsheets indeed have their merits for specific tasks and data operations, excessive reliance on Excel as the primary data repository presents significant challenges, especially for healthcare organizations. In this section, we will explore the pitfalls of storing substantial volumes of critical data in Excel rather than utilizing a traditional database. Let’s delve deeper into these concerns:
Errors and Inconsistencies ❌?
Excel spreadsheets are prone to human error and inconsistency, which can lead to critical mistakes in medical records. These errors can range from simple data entry mistakes to complex formula errors that affect calculations in medical reports.
| As an illustration, autocorrect errors in Excel continue to pose challenges in the field of genomics. Despite prior warnings to geneticists regarding spreadsheet-related issues, approximately 30% of published papers still exhibit distorted gene names within their supplementary data. |
Medical Document Version Control Issues ??
Collaborating on Excel or similar sheets often results in version control problems, making it difficult to track changes accurately. When multiple individuals edit the same spreadsheet, it’s challenging to maintain a clear, up-to-date record of modifications.
The FDA mandates adherence to 21 CFR Part 11, which necessitates comprehensive tracking of data modifications. When alterations occur in a spreadsheet, change history, including the user responsible, date and time, previous vs. new values, and the reason for the modification must be documented. Excel and other older products lack the audit trail functionality required for this type of compliance.

Lack of Security ??
Excel files are susceptible to security breaches, posing a significant risk to patient confidentiality and HIPAA compliance. Unauthorized access to files can compromise sensitive patient data, leading to legal and ethical concerns.
Limited Scalability ??
As healthcare organizations grow, Excel becomes less scalable and unable to handle the increasing volume of medical documents. It’s challenging to maintain a centralized, organized repository of documents as an organization expands.
Data Integrity ??
Ensuring data integrity in Excel-based systems is challenging. Without proper data validation and auditing mechanisms, there is a higher likelihood of data corruption, which can lead to inaccurate medical records and compromised patient care.
Ineffective Workflow Management ??
Spreadsheets often fall short when it comes to ensuring organizations’ adherence to standard operating procedures (SOPs) and regulatory requirements governing documentation and workflow. Excel, at its core, serves as a manual tool for tracking documentation status, typically relying on email exchanges and meetings for data collection. Consequently, real-time status updates are infrequent and accuracy remains a challenge.
The Benefits of Medical Document Automation
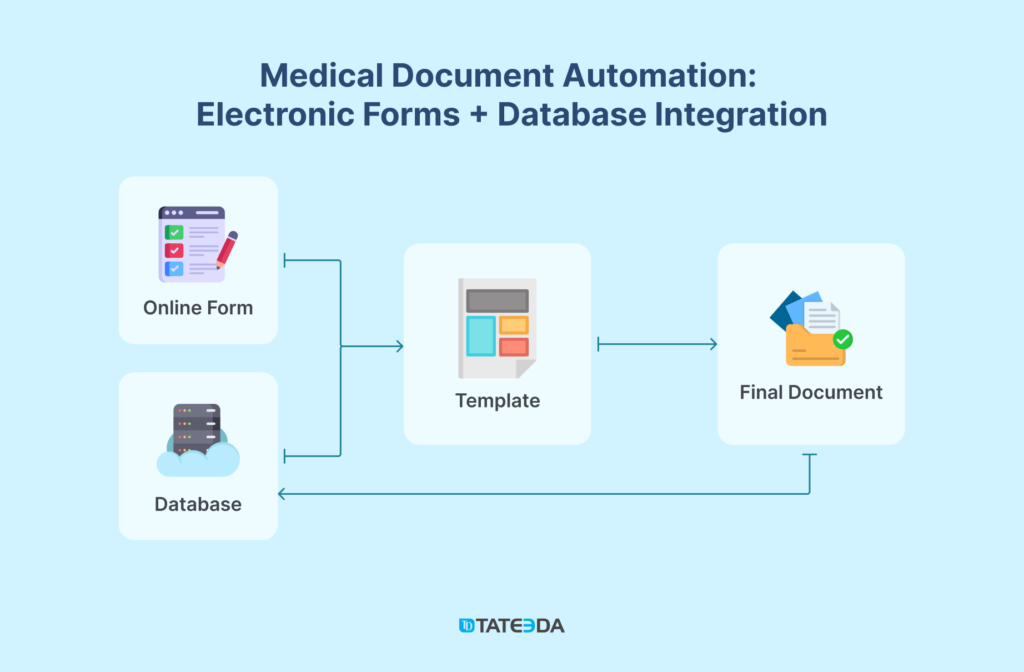
Let’s outline succinctly the concept of document automation in healthcare. Its fundamental components include:
- Online Electronic Form: The initial data input interface for authorized users.
- Database + Server: Backend infrastructure that stores and manages data.
- Automated Document Template: The pre-defined format for generating documents, including intelligent or algorithmic fields.
- Recording the Final Document: The process of saving the completed document back to the database, governed by specific user roles and permissions.
| Benefits | Effects |
| Enhanced Accuracy | Automation ensures precise data entry and reduces the risk of error in medical documents. Automation tools can be programmed to validate data at point of entry, flagging any discrepancies for immediate correction. |
| Efficiency and Accessibility | Automation provides instant access to medical records, speeding up decision-making processes. Authorized personnel can retrieve patient information quickly, leading to faster diagnosis and treatment. |
| HIPAA Compliance | Automation tools can be designed with robust security features to maintain compliance with healthcare regulations like HIPAA. These features include encryption, access controls, and audit trails to monitor and protect patient data. |
| Streamlined Workflows | Automation streamlines document-related workflows by automating tasks such as data extraction, categorization, and routing. This reduces administrative overhead, allowing healthcare professionals to focus on patient care. |
| Cost Savings | Over time, medical document automation can lead to significant cost savings. It reduces the need for manual data entry, reduces the risk of errors that can result in legal liabilities, and optimizes resource allocation. |
? NOTE: If you want to adopt healthcare document automation in your organization, please take a moment to learn more about our services and capabilities:
Custom Healthcare Solutions
See how we can engineer healthcare software, validate your ideas, and manage project costs for you.
Automation Tools and Solutions
Each of these methods of healthcare documentation automation plays a vital role in modernizing healthcare processes, improving patient care, reducing errors, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Choice of automation tools and methods depends on the specific needs and goals of each healthcare organization:
- Electronic Health Record (EHR) Systems: Custom EHR system development offers comprehensive solutions that integrate patient records, medical history, and billing information into a single platform. These systems offer a centralized repository for all patient-related information, ensuring easy access and efficient management. If you want to learn more about EHR and EMR systems, check our comprehensive guide on creating electronic health records software.
- Document Management Software: Specialized document management software offers features like document categorization, searchability, and automated workflows. It enables healthcare organizations to organize, secure, and retrieve medical documents with ease.
- Data Extraction Tools: Data extraction tools use optical character recognition (OCR) and machine learning algorithms to extract relevant information from medical documents. This technology automates the process of capturing data from paper-based documents, thereby reducing manual data entry effort.
- Workflow Automation Platforms: Workflow automation platforms allow healthcare organizations to create custom workflows for document management. These platforms enable the automation of repetitive tasks such as document routing, approvals, and notifications.
- Automated Coding and Billing: Automated systems can code diagnoses and procedures based upon patient records, reducing coding errors and ensuring accurate billing. This is crucial for healthcare reimbursement and financial management. If you require further consultation regarding the custom development and integration of healthcare billing systems, please do not hesitate to contact our skilled team.
- Health Information Exchange (HIE): HIE systems allow secure sharing of patient data between different healthcare organizations and providers. This promotes interoperability (including HL7 technology) while ensuring that critical patient information is accessible when needed.
- Intelligent Document Processing (IDP): IDP combines AI and automation to extract and process data from medical documents. It can categorize documents, extract relevant information, and route them to the appropriate systems.
- Secure Cloud Storage: Cloud-based medical automation solutions provide secure storage for medical records and documentation. Cloud platforms offer scalability, accessibility, and disaster recovery capabilities.
Implementing Medical Document Automation
Design the Mobile/Web Forms and Document Templates: ???
- Create intuitive interfaces for mobile and web forms to facilitate efficient data input by healthcare staff.
- Optimize templates to streamline data input and document generation, reducing error and manual effort.
- Ensure that forms and templates are responsive across devices, enhancing accessibility and usability.
Migrate from Excel to a Database Solution: ?
- Evaluate existing data structure and relationships.
- Choose an appropriate database system.
- Develop a data migration plan and perform a test migration.
- Plan the data migration process meticulously to prevent errors.
- Perform an audit and cleansing of medical document data before migration.
- Implement medical and operational data validation and backup procedures.
- Take specific precautions if cloud migration of medical data is involved.
- Implement the migration during a low-activity period and ensure data integrity.
Staff Training: ?
- Provide training on EHR systems, document management software, and data extraction tools.
- Offer ongoing training and support for updates.
Integration with Existing Systems: ?
- Ensure seamless integration with EMRs, prioritizing the synchronization of patient data.
- Validate data consistency and compatibility between the new database solution and existing systems.
- Implement data-sharing protocols and APIs to facilitate real-time data exchange.
- Conduct thorough testing to confirm that data is accurately transferred and synchronized across all integrated systems.
Change Management: ?️
- Acknowledge that implementing medical document automation represents a significant workflow change for healthcare organizations.
- Align human factors with all changes and effectively communicate the benefits while addressing concerns to ensure a smooth transition.
Compliance Assessment: ?
- Conduct a comprehensive assessment to align with regulatory requirements.
- Include considerations for data retention and disposal policies.
? NOTE: If you’re considering adopting document automation for healthcare purposes, please browse through our project portfolio:
Delivered Healthcare Software Portfolio
The leading American healthcare companies benefit from working with us.
Case Study: Medical Automation Solution for a Pharma Company
In the realm of healthcare, specifically pharmacy prescription documentation automation, a range of features play a pivotal role. One prominent feature is OCR-based processing, which scans PDF attachments to extract vital data such as keywords and pricing information. Additionally, this type of system automatically generates PDF reports based on the data found in these claims.
It doesn’t stop there. Automatic alert notifications come into play when specific prescription drugs and/or price/dosage combinations are detected. Managing this intricate process is made user-friendly by a dedicated UI component for handling email replies, PDF templates, and alert parameters.
This comprehensive functionality revolutionizes a wide range of tasks within healthcare operations:
- Claim Processing: By harnessing OCR-based processing, essential data from PDF claims, including patient details, prescription information, and pricing, is effortlessly extracted. This data serves as the foundation for automated claim-processing.
- Report Generation: Automated PDF report generation empowers healthcare providers to effortlessly generate insightful reports. Metrics such as claim processing volumes, average processing times, and overall costs can be effortlessly calculated and conveyed.
- Alerting: Your system’s automatic alert notifications are instrumental in flagging potential issues. Whether it’s a claim missing crucial information or one that surpasses a predefined cost threshold, staff members can be instantly alerted.
- Data Management: The UI component, which facilitates management of email replies, PDF templates, and alert parameters, is an invaluable tool for maintaining and fine-tuning the data underpinning any document automation process.
- CSV Import: Your system’s capability to import and process data from CSV files, complete with alert notifications, streamlines the processing of claims submitted in this format.
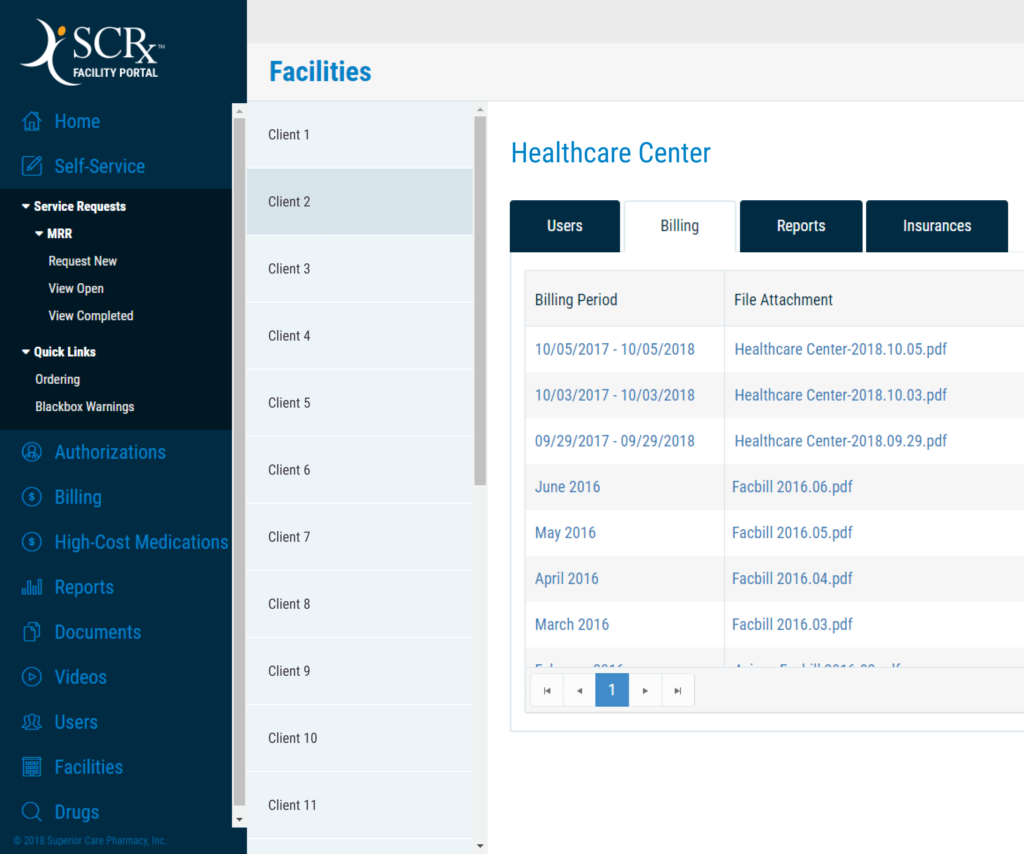
In summary, document automation revolutionizes pharmacy claim processing and medication fulfillment in healthcare. It boosts efficiency, reduces costs, and enhances precision and reliability.
? NOTE: If you’re considering adoption of document automation for healthcare purposes, please contact us →
Future Trends in Medical Document Automation
AI and Machine Learning: These technologies are poised to transform medical document management by automating tasks like data extraction and classification. AI algorithms can analyze medical records, recognize patterns, and assist in diagnosis of medical conditions. Machine learning models can continuously improve document categorization and search capabilities.
Intelligent Document Processing (IDP): IDP combines AI and automation to intelligently process documents, making information retrieval even more efficient. It can automatically extract structured and unstructured data from documents, allowing for better data analysis and decision-making.
Blockchain in Document Security: Blockchain technology can enhance the security and integrity of medical documents, ensuring authenticity and traceability. Each document can be cryptographically signed and timestamped, creating an immutable record. This technology can also facilitate secure data-sharing among healthcare providers while maintaining patient privacy.
Telemedicine Integration: As telemedicine continues to grow, the integration of medical document automation with telehealth platforms becomes essential. Patients’ medical records must be readily accessible to healthcare providers during virtual appointments, making automation a key component of telemedicine.
Predictive Analytics: Combined with predictive analytics, medical document automation can help healthcare organizations forecast patient needs, disease outbreaks, and resource allocation. By analyzing and mining historical medical data, healthcare providers can make data-driven decisions and improve patient care.
FAQ: Medical Document Automation Development
How does medical document automation assist in maintaining compliance with healthcare regulations like HIPAA?
Medical document automation tools often include robust medical data security features such as encryption and access controls which ensure that patient data remains confidential and compliant with regulations like HIPAA. Automated audit trails also assist in tracking and documenting access to sensitive patient information. Learn more: ➡️ Medical Staffing Software Compliance: How to Achieve HIPAA Validity
What are some key considerations for data migration when transitioning to an automated system?
Data migration should prioritize data integrity, ensuring that all medical records are transferred accurately. To minimize disruptions, it’s essential to plan for data cleansing, validation, and backup procedures. Additionally, thorough testing of migrated data is crucial to identify and rectify any discrepancies.
Are there any risks or drawbacks to be aware of when implementing medical document automation?
While the benefits are substantial, implementation challenges can include initial costs, staff training, and the potential for workflow disruptions during transition. Careful planning can mitigate these risks. Additionally, organizations should be prepared for ongoing maintenance and updates to ensure continued effectiveness of automation systems.
How can AI and machine learning benefit medical document management in the future?
AI and machine learning can automate data extraction, classification, and analysis tasks, significantly reducing the time and effort required to manage medical documents. This can enhance accuracy and decision-making processes within healthcare organizations. Furthermore, these technologies have the potential to assist in diagnosis of medical conditions and prediction of patient outcomes based on historical data, thus leading to improved patient care and outcomes.



![Moving to the Cloud for Healthcare Companies [Step-by-Step]](https://tateeda.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/cover-image.png)